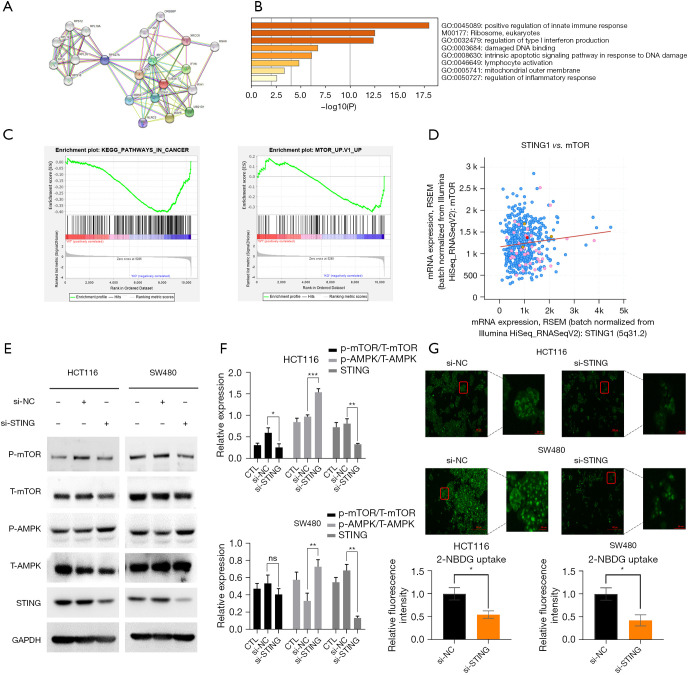
Figure 3.
STING regulates biological characteristics through the AMPK-mTOR pathway and glucose uptake in CRC cells. (A-C) GSEA was conducted using gene sequencing data from the GEO GSE129436 and 100179 data sets (KEGG enrichment, tumor-associated pathways). (D) cBioPortal indicated that STING is closely related to the mammalian target of the rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in CRC. (E) 48 hours after the transfection of STING siRNA and the negative control siRNA, the expressions of p-mTOR, T-mTOR, p-guanosine monophosphate-adenosine 5’-monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK), T-AMPK, and STING were detected by Western blot assays. (F) For the quantitative analysis of the gray value of results in (E), we repeated the experiment three times. (G) A glucose fluorescent probe was used to detect the glucose uptake of the HCT116 and SW480 CRC cells. Average fluorescence intensity was quantified by randomly selecting 5 microscopic fields. P<0.05 was considered statistically significant. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, and ***P<0.001. CRC, colorectal cancer; GSEA, Gene Set Enrichment Analysis; GEO, Gene Expression Omnibus; KEGG, Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes; NC, normal control; CTL, control; STING, stimulator of interferon genes.