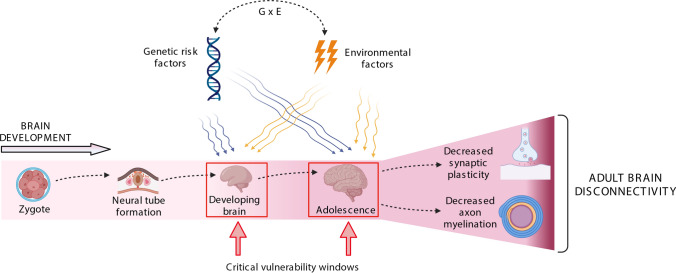
Fig. 1.
Impact of genetic and environmental factors during neurodevelopment in schizophrenia: two vulnerable periods in brain development are the prenatal period and adolescence. During these critical periods, genetic and environmental risk factors of schizophrenia act together to induce deficits in synaptic plasticity and myelination. As consequence, impaired micro- and macroconnectivity is the basis of cognitive deficits and symptoms of the disease, which arise in young adulthood