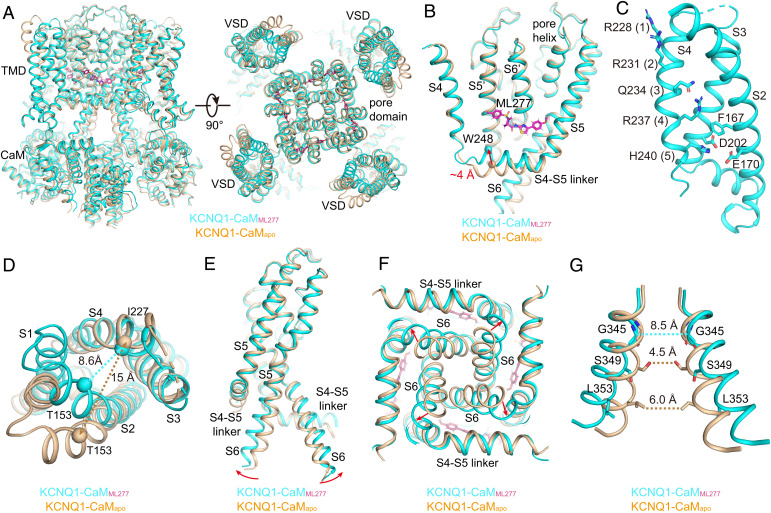
Fig. 5.
ML277-induced conformational changes of KCNQ1. (A) Structural comparison of KCNQ1-CaMapo (wheat) and KCNQ1-CaMML277 (cyan) in the side view (Left) and top view (Right). (B) ML277 induces an upward movement of the S4-S5 linker. Arrow indicates the distance between the N-terminal residue Trp248 in the S4-S5 linkers in two structures. (C) The VSD in KCNQ1-CaMML277 with S1 omitted for clarity. Side chains of gating charge residues and residues forming the CTC are shown as sticks. (D) Structural differences of VSDs in KCNQ1-CaMapo (wheat) and KCNQ1-CaMML277 (cyan) in the top view. The dashed lines show the distances between Cα atoms of Thr153 in S2 and Ile227 in S4 in two structures. (E) Structural differences of PDs in KCNQ1-CaMapo and KCNQ1-CaMML277 in the side view. For clarity, only two opposing subunits are shown. Red arrows indicate the outward bending of S6 C-terminal halves upon ML277 binding. (F) Structural differences of PDs in KCNQ1-CaMapo and KCNQ1-CaMML277 in the bottom view. (G) Structural differences of the activation gates in KCNQ1-CaMapo and KCNQ1-CaMML277 in the side view. The dashed lines show diagonal atom-to-atom distances between constriction-forming residues (in Å). The gate in KCNQ1-CaMML277 opens up.