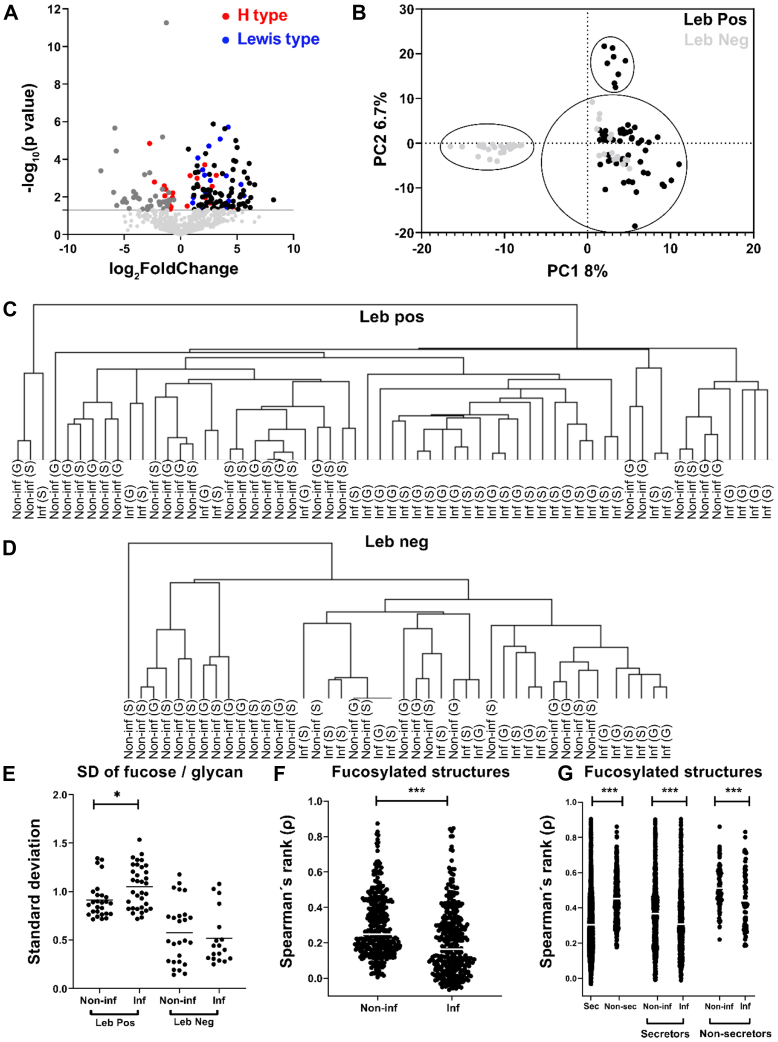
Fig. 5.
Distribution of Lewis structures and fucosylation on mucins from individuals with and without Helicobacter spp. infection.A, volcano plot of differentially expressed gastric glycans between noninfected and Helicobacter spp.-infected individuals (mean of all four mucin fractions). Dots to the left of zero denote glycans expressed predominantly in noninfected individuals. Dots to the right indicate glycans more expressed in infected individuals. Red dots denote H-type structures, and blue dots denote Le-type structures (Leb/y and Lea/x). The horizontal gray line indicates p = 0.05. Below this line, the light gray represents glycans that were not differentially expressed. B, principal component analysis (PCA) based on O-glycan relative abundances (RAs) for all samples. Each dot represents a mucin source from each individual (X-variables; n = 631). The black dots indicate Leb positive, and gray dots represent Leb-negative samples based on ELISA. C and D, dendrogram after hierarchal clustering of Lewis structures from human mucins from surface (S, mean of SS + SI) and gland (G, mean of SD + ID) isolated from noninfected (Non-inf) and infected (Inf) stomachs. E, the standard deviation of the number of fucose per glycan in Leb-positive and Leb-negative samples. The bars represent mean, and significance was calculated using two-way ANOVA. F, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (ρ) of the RA of the gastric surface fucosylated glycans. G, Spearman's rank correlation coefficient (ρ) of the RA of the gastric surface fucosylated glycans grouped based on secretor (sec) status. The bars represent the median, and significance was calculated using the Mann–Whitney U test. ∗ and ∗∗∗ indicate p < 0.05 and p < 0.0001, respectively. SI, surface insoluble; SS, surface soluble.