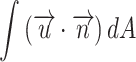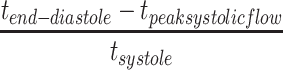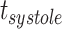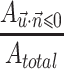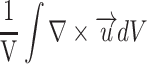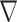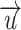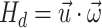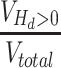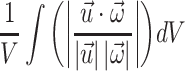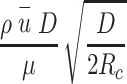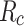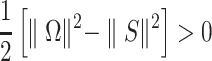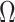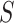Table 2.
Summary of 4D flow-derived metrics
| Category | Metric | Definition | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Geometry & Stiffness |
PA volume, V (ml) | Temporally averaged volume of the MPA, LPA, RPA branches over a cardiac cycle | Internal diameters potentially influenced by proximal thrombus |
| PA area, A (cm2) | Centerline-based cross-sectional slice located 50% down the length of the MPA, LPA, and RPA branches | ||
| Relative area change (Pulsatility) |
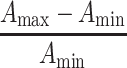
|
||
| Compliance (cm2/mmHg) |
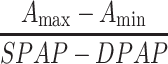
|
Healthy PA compliance = 0.15 cm2/mmHg§ | |
| Distensibility (%/mmHg) |
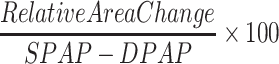
|
Healthy PA distensibility = 3.1%/mmHg§ | |
| Velocity Flow Profile | Centerline velocity (cm/s) | Maximum velocity in the center 30% radius of a cross-sectional slice located 50% down the length of each branch. | |
| Flow rate (L/min) |
|
||
| Acceleration ime ratio |
|
||
| Secondary Flow Profile | Fractional area of reverse flow |
Areas where velocity is perpendicular or negative to the forward flow direction.
Taken at a cross-sectional slice 50% down the length of the branch |
Quantifies areas of recirculation, may correspond to large visual vortices |
Vorticity, 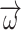 (1/s) (1/s) |
|
Local rotation in a fluid flow including local shearing in space | |
| Helicity density, Hd (m/s2) |
Amount of rotation parallel to the local velocity vector |
Clockwise rotation when 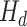 >0, counterclockwise rotation when >0, counterclockwise rotation when 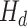 <0 <0 |
|
| Volume fraction of positive helicity |
V is the volume of the branch |
||
| Helical flow index, HFI |
Absolute value of the cosine of the angle between the vorticity and velocity vector, measure of helicity intensity |
Limit from 0 to 1 | |
| Dean number, De |
D is the diameter of the vessel, |
Non-dimensional parameter of the inertial, centripetal, and viscous forces; tendency of Dean vortices to form in a curved vessel | |
| Q-criterion |
Defines a vortex as a connected fluid region where the norm of the vorticity tensor, |
May not uniquely detect visual vortical regions | |
| RV Function§§ | % Predicted RV metrics |
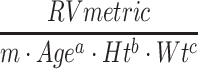
|
Adjusted for differences in sex, age, weight, height |
|
RVEF: a = 0.0706, b=-0.00771, c=-0.0782 m = 75.19 (female), 71.52 (male) | |||
|
RVEDV: a=-0.258, b = 1.582, c = 0.382 m = 27.94 (female), 31.50 (male) | |||
|
RVESV: a=-0.417, b = 1.501, c = 0.617 m = 5.58 (female), 7.24 (male) | |||
|
RVSV: a=-0.187, b = 1.574, c = 0.304 m = 21.12 (female), 22.42 (male) |
§Healthy PA compliance and distensibility from Sanz et al. [29]
§§RV metrics were adjusted for sex, age, weight, and height based on normalized equations from Kawut et al. [27]. RV, right ventricle, EF, ejection fraction, EDV, end-diastolic volume, ESV, end-systolic volume, SV, stroke volume, PA, pulmonary artery