Figure 5.
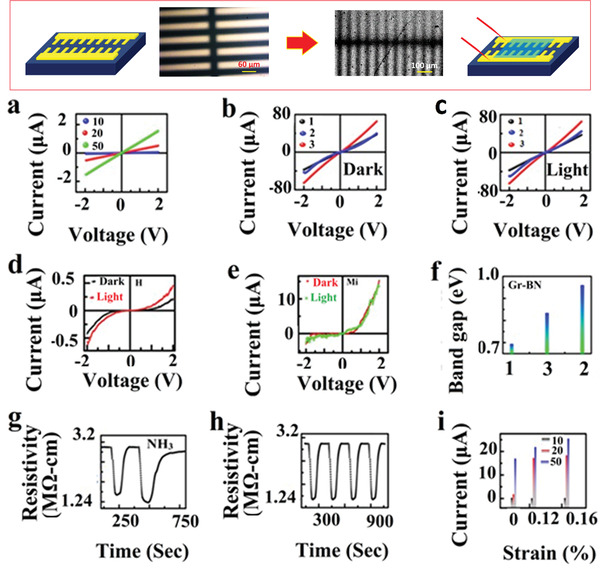
a) Two probe I–V measurements of hybridized RGO‐RBNO wt% at (10, 20, and 50) samples spin‐coated on PET substrate, conductivity increased with increasing % of RGO in BN from 0.1 to 1.8 µA. b,c) In‐plane I–V measurements with and without a light source for (GBNH, GBNS, GBNM) hybridized samples, GBNM hybrid exhibited the highest current values 65 µA with semiconducting nature compared to GBNS (40 µA) and GBNH (35 µA), and the highest photocurrent response was recorded for GBNS ≈46 µA. d,e) I–V measurements out‐of‐plane for GBNM and GBNS exhibited tunneling currents of 15 and 0.3 µA in the dark; upon exposure to blue light, it exhibited current values of 12 and 0.5 µA with semiconducting behavior. f) Electronic band gaps were calculated from R versus T measurement, highest bandgap was obtained for the GBNS sample of 0.96 eV compared to 0.83 eV for GBNM and 0.69 eV for the GBNH sample. g,h) Gas sensing behavior of hybridized RGO‐RBNO sample was studied upon exposure of analyte ammonia gas at different concentrations (70 and 100 PPM). Its repeatability behavior was demonstrated for five cycles at 70 PPM. i) Straintronics behavior was recorded for hybridized RGO‐RBNO samples (10, 20, and 50) wt% for spin‐coated on PET substrate, 50% RGO in BN sample exhibited the highest current from 2 to 17 µA when strain changed from 0% to 0.16%. Optical and SEM images of the device used for electrical measurements are shown in the top panel.
