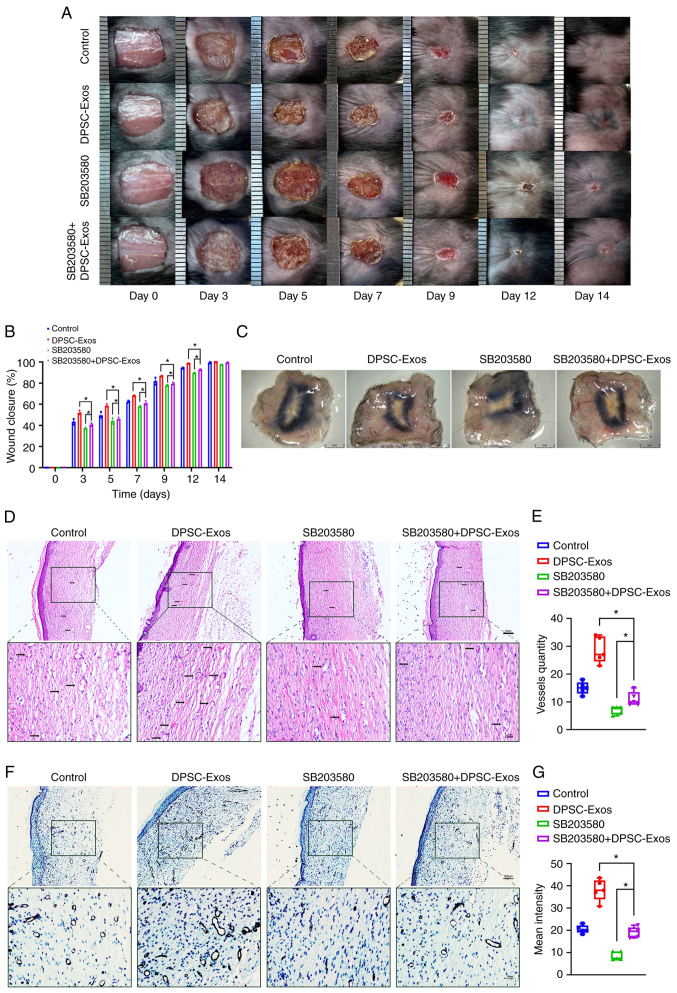
Figure 5.
DPSC-Exos accelerate cutaneous wound healing in mice via p38 MAPK. (A) Gross view and quantification of the wound area of mice treated with DPSC-Exos in the presence or absence of SB203580 on days 3, 5, 7, 9, 12 and 14 post-wounding. Scale bar, 1 cm. (B) The rate of wound closure in wounds receiving DPSC-Exos or PBS treatments in the presence or absence of SB203580 at the indicated time points (n=3). (C) Gross view of wounds treated with PBS and DPSC-Exos in the presence or absence of SB203580 on day 14 post-wounding from the undersurface. Scale bar, 2 mm. (D and E) Hematoxylin and eosin staining of wound sections treated with PBS and DPSC-Exos in the presence or absence of SB203580 at 14 days after the operation (n=3). The black arrows indicate newly formed blood vessels. Scale bar, 100 µm. (F and G) Immunohistochemical staining for CD31 in wound sections treated with PBS and DPSC-Exos in the presence or absence of SB203580 at 14 days after the operation (n=3). Scale bar, 100 µm. *P<0.05. DPSC, dental pulp stem cell; Exo, exosome; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline.