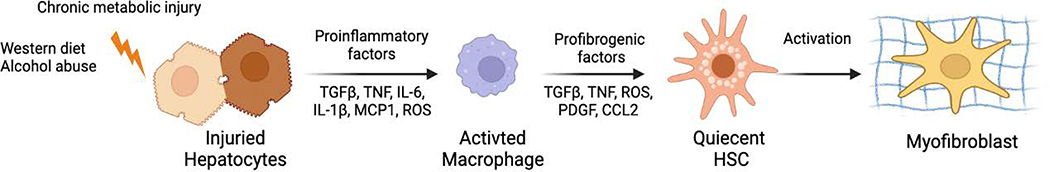
Figure 1. Pathogenesis of toxic liver fibrosis and therapeutic implications.
Hepatocyte damage triggers the inflammatory response, leading to activation of macrophages, release of ROS and TGFβ1, and activation of quiescent HSCs into activated HSCs/myofibroblasts that produce collagen type I resulting in liver fibrosis.