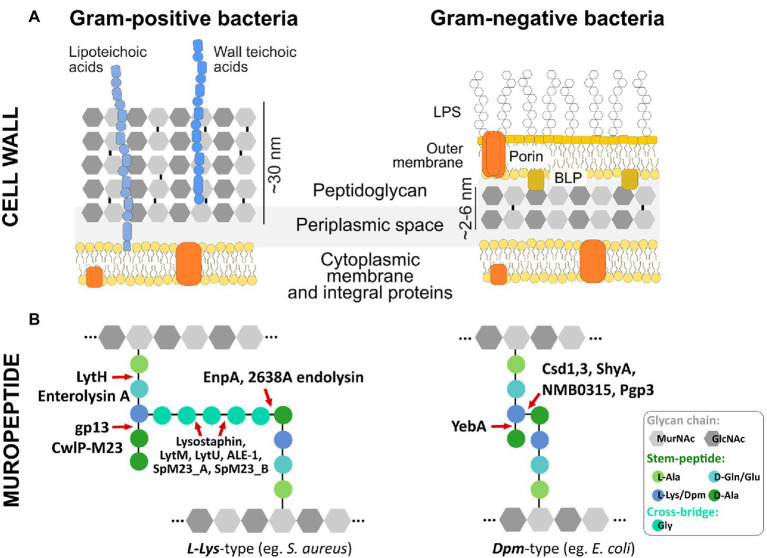
Figure 1.
Bacterial cell wall architecture, peptidoglycan composition, and M23 hydrolytic enzymes dedicated to different bonds in PG structure (A) Schematic representation of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria cell wall. (B) Basic building blocks and crosslinking of peptidoglycan layer depicted for representative species of Gram-positive (e.g., S. aureus) and Gram-negative (e.g., E. coli) bacteria. M23 peptidases are presented as enzymes dedicated to cleaving specific bonds in peptidoglycan structures of both L-Lys-type and Dpm-type peptidoglycan. Glycan chains of N-acetylmuramic acid (MurNAc) and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) are depicted as gray hexagons; integral membrane proteins are colored in orange; D- and L-amino acids and Dpm (meso-diaminopimelic acid) characteristic for the stem peptide and cross-bridge are presented as colored circles; LPS, lipopolysaccharides; BLP, Braun’s lipoprotein (Vollmer et al., 2008).