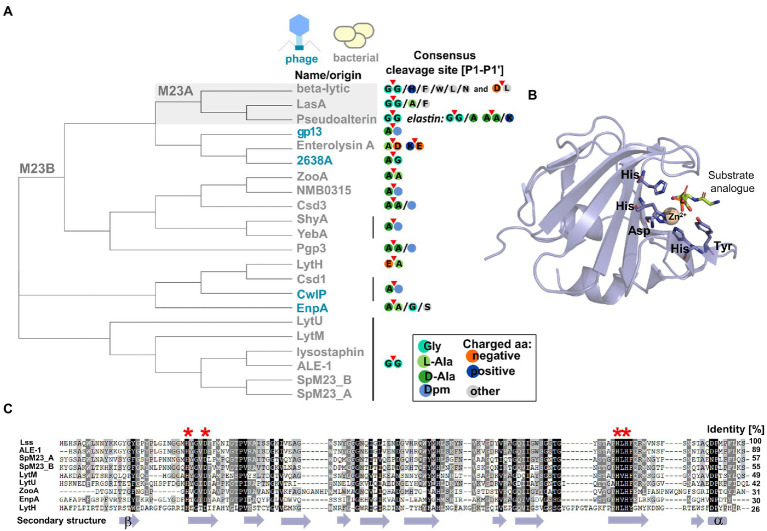
Figure 2.
Characteristic features of M23 peptidases. (A) Phylogenetic analysis represented as a cladogram of M23 peptidases of phage (colored blue) or bacterial (colored gray) origin with their specificities. M23A subfamily was indicated against gray background. According to the nomenclature of protease substrate specificity defined by Schechter and Berger (Schechter and Berger, 1967), amino acid residues in the peptide substrate sequence are consecutively numbered outward from the cleavage sites as P4-P3-P2-P1-P1’-P2’-P3’-P4’ and the scissile bond is located between the P1 and P1’ positions (here marked with red triangle). (B) Overall fold of M23 peptidase domain represented by LytM catalytic domain (PDB ID: 4ZYB). The structure was solved in the presence of the transition state analogue and zinc ion coordinated by conserved motifs: Hx3D and HxH. (C) Multiple sequence alignment performed by ClustalX and presented as Gendoc of M23B representative proteins with highly conserved zinc-binding motifs (depicted in red asterisk on the top of alignment) and secondary structure elements (depicted in violet at the bottom) assigned by PROMALS3D program (Larkin et al., 2007; Pei et al., 2008).