Figure 9. Outline of the system preparation steps.
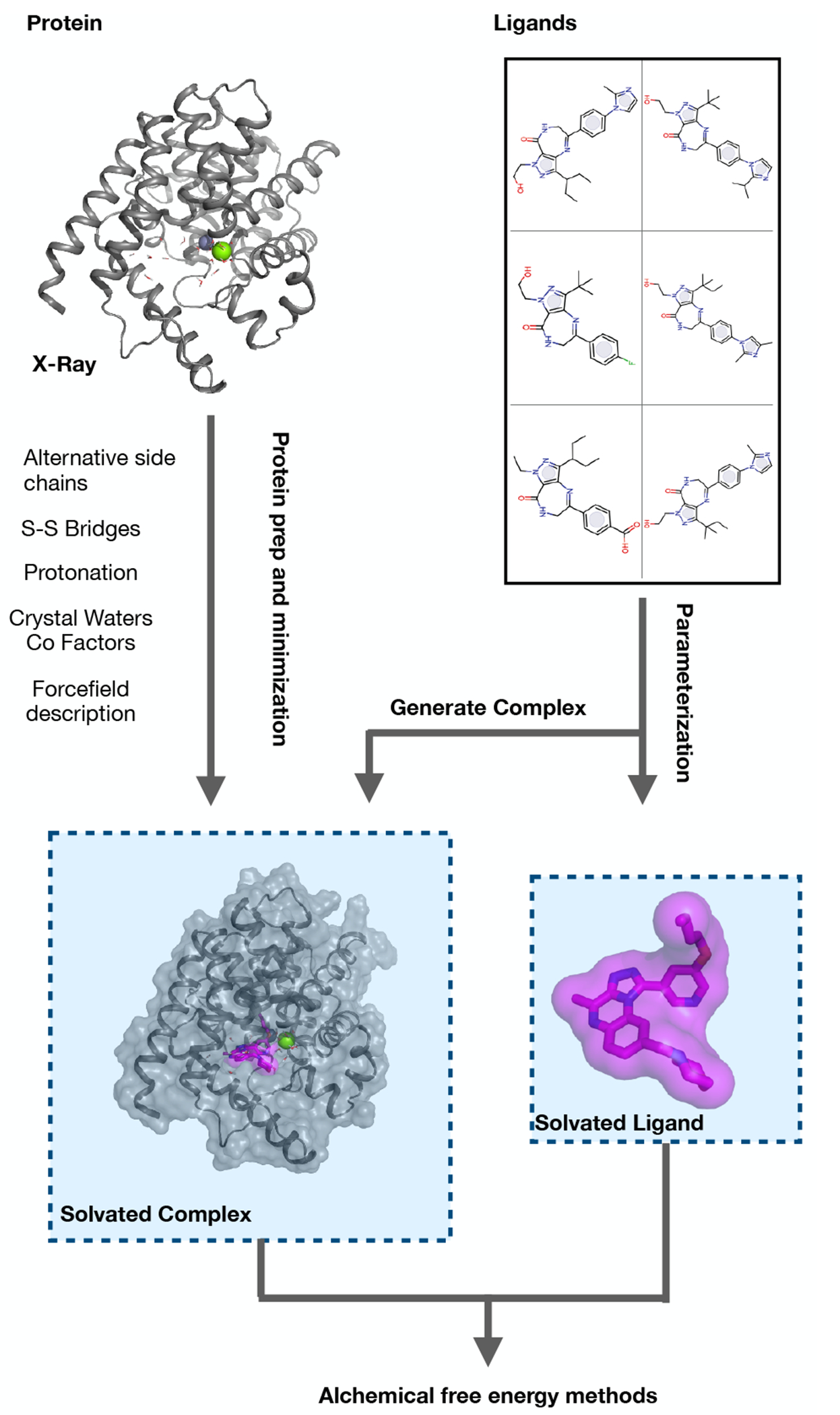
First the protein is prepared (left, Section 5.1.1) by modelling missing atoms, assigning bond orders, protonation and tautomeric states. Similarily, the chemical structure of the ligands is translated into a simulation model (right, Section 5.1.2). The ligands are simulated in two different environments, once complexed with the protein (bottom left) and once in solvent (bottom right). For the solvated complex, the ligand structures need to be docked into the binding site of the protein, typically by using the information of a reference ligand in the X-ray structure.
