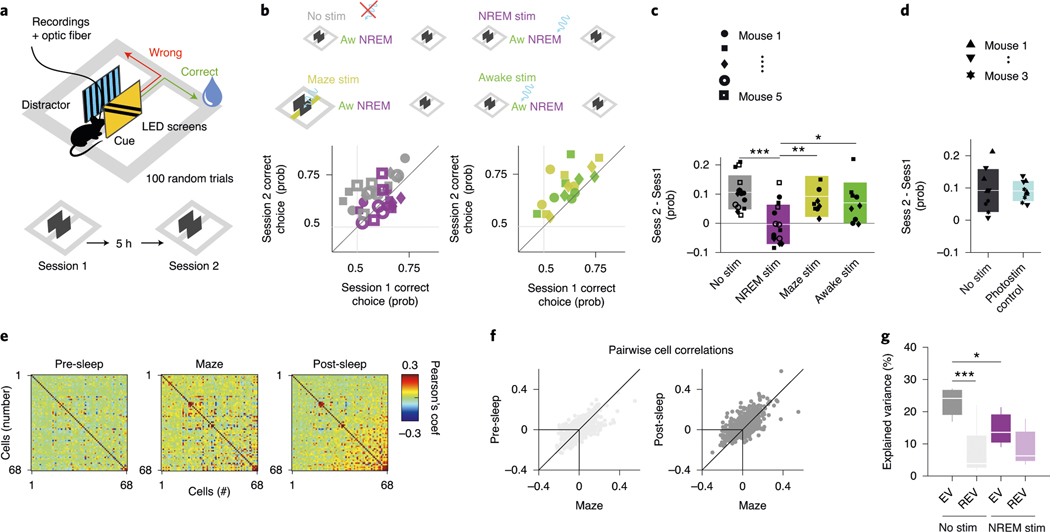
Fig. 7 |. Perturbation of DSA neurons during NREM sleep impairs memory consolidation.
a, Diode probes were implanted bilaterally in the PPC in ID2/Nkx2.1::CatCh mice. They performed in a goal-associated visual cue discrimination task (for example, blue and yellow stripe patterns) twice daily (morning and afternoon sessions). b, Performance of each mouse in the morning (session 1) and afternoon (session 2). On randomly chosen days, mice were left unperturbed in the home cage between sessions (gray symbols) or ID2/Nkx2.1 neurons were optogenetically stimulated (100-ms duration light pulses every 500 ± 400 ms) during NREM sleep (purple). As further controls, the same optogenetic stimulation during wake in the home cage (green) or during the task in the central arm continuously (yellow) did not interfere with sleep-induced memory improvement. Each symbol depicts a comparison between morning (session 1) and afternoon (session 2) sessions (3-d per condition). c, Only optogenetic perturbation of ID2/Nkx2.1 neurons during NREM sleep affected memory consolidation (mean ± s.d., P = 0.001, KW test; P < 10−4 for ‘No stim’ against ‘NREM stim’, Tukey test). d, Same stimulation protocol in a different cohort of animals that lacked Chr (‘photostimulation control’) did not affect memory consolidation (mean ± s.d.; n = 3; P = 0.8946, KW test). e, Example of rate correlation matrices for all neuron pairs from pre-NREM sleep, maze (first session) and post-NREM sleep in an example mouse (non-stimulation, control day). These matrices were used to calculate the EV and its control value, the reverse explained variance (REV), in both non-stimulated and optogenetically stimulated sessions. f, Pearson correlation coefficients for all neuron pairs for pre-sleep versus maze learning (left) and post-sleep versus maze learning (right) comparison (same example session as in e). g, Group statistics (medians, interquartile ranges, maxima and minima; n = 5 mice, at least one session per animal) of the EV and REV on non-stimulated (control) and NREM-stimulated (P = 0.002, KW test) days. EV on non-stimulated days was significantly higher than its corresponding REV (chance, P = 0.003, Tukey test) and also significantly higher than EV on NREM-stimulated days (P = 0.012). *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001.