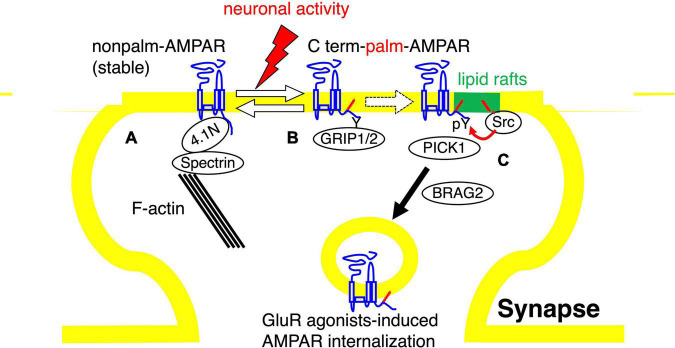
FIGURE 3.
Model of the role of AMPA receptor palmitoylation in lipid rafts. Diagram of the role of AMPA receptor palmitoylation and tyrosine phosphorylation. (A,B) The balance between palmitoylated and de-palmitoylated forms of the AMPA receptor can be regulated by glutamate receptor agonists treatment, suggesting that synaptic activity can regulate the steady-state level of AMPA receptor palmitoylation. De-palmitoylation of the AMPA receptor on the C-terminal site increases the receptors’ affinity for 4.1N, which stabilizes AMPA receptors at the synaptic surface by the interaction of 4.1N with F-actin and spectrin (A). In contrast, the palmitoylated forms of surface AMPA receptors are less stably associated with the synaptic membrane and are more susceptible to neuronal activity-induced internalization (B). (C) The palmitoylated AMPA receptors are assumed to translocate to the synaptic membrane lipid rafts, where the palmitoylated Src family protein tyrosine kinases are concentrated. Phosphorylation of GluA2 at Tyr876 by Src family protein tyrosine kinases induces the exchange of AMPA receptor-binding proteins from GRIP1/2 to PICK1 and the receptor interaction with BRAG2, which drive endocytosis of surface AMPA receptors.