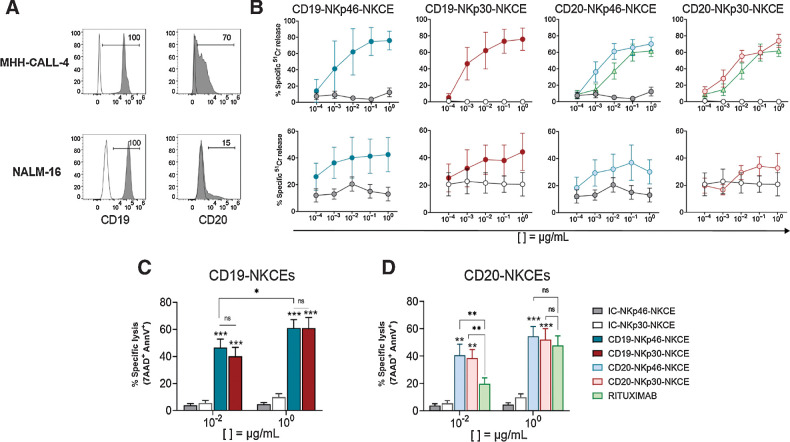
Figure 1.
Effect of NKCEs targeting CD19 or CD20 on BCP-ALL cell lines. A, Two pediatric BCP-ALL cell lines were characterized for the surface expression of CD19 and CD20 via flow cytometry using specific mAbs followed by PE-conjugated anti-IgG1 secondary reagent. Numbers represent the percentage of positive cells. B, Comparison of cytotoxicity (51Cr-release assay) of resting NK cells from healthy donors against MHH-CALL-4 (top row, n = 2–6) or NALM-16 (bottom row, n = 3) cells in the presence of NKCEs at the indicated concentrations (see legend for color symbols in D). E:T ratios were 10:1 and 5:1 for MHH-CALL-4 cells and NALM-16 cells, respectively. Percent of specific lysis, via 7AAD/AnnV staining, of MHH-CALL-4 cells cocultured with resting NK cells from healthy donors (n = 4–9) in the presence of CD19-NKCEs or IC-NKCEs (C), and CD20-NKCEs, IC-NKCEs, or rituximab (D) at 10−2 μg/mL and 100 μg/mL. Results from 6–10 independent experiments are reported. In both cytotoxicity assays, 4-hour coculture was performed. Bars show mean ± SEM. Statistical significance: *, P ≤ 0.05; **, P ≤ 0.01; ***, P ≤ 0.001. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test was used to calculate statistical differences among the indicated NKCEs within each concentration. Mann–Whitney test was used to compare each NKCE at the two indicated concentrations.