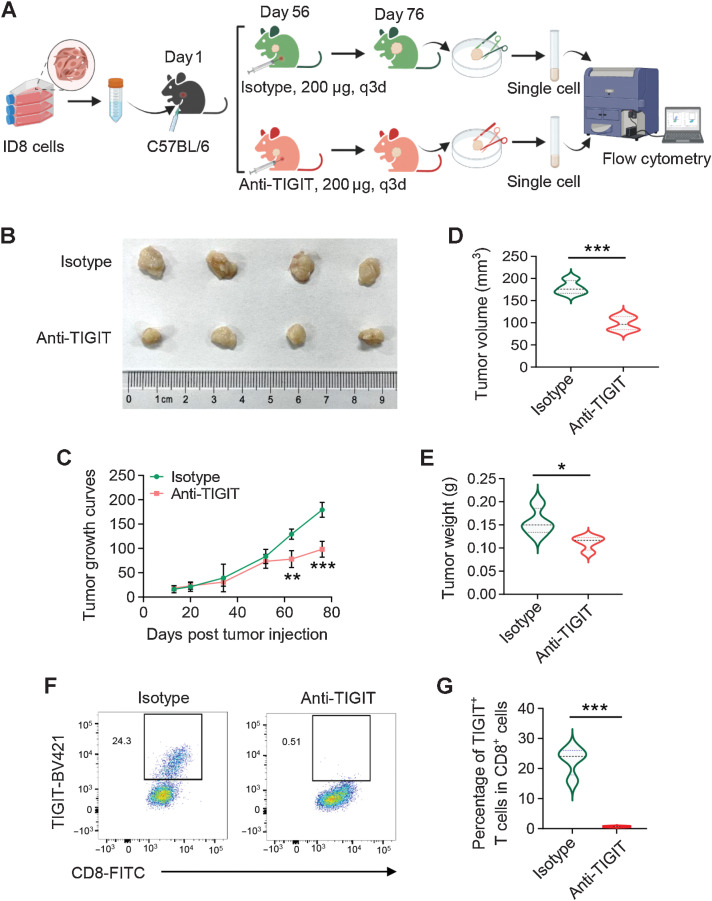
Figure 6.
Blockade of TIGIT inhibits tumor growth in syngeneic mice. A, Workflow showing the experimental process of the animal study. B, C57BL/6 mice were subcutaneously injected with ID8 cells (5 × 106 per mouse) and treated with 200 μg anti-TIGIT or isotype-matched control antibody via intraperitoneal injection as indicated. Tumor growth curves (C), tumor volume (D), and tumor weight (E) at the endpoint were measured. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. F and G, Frequency of TIGIT+-CD8+ T cells from tumors in anti-TIGIT or isotype-matched control antibody-treated mice by flow cytometry. Data are mean ± SD (n = 4 mice/group). ***, P < 0.001.