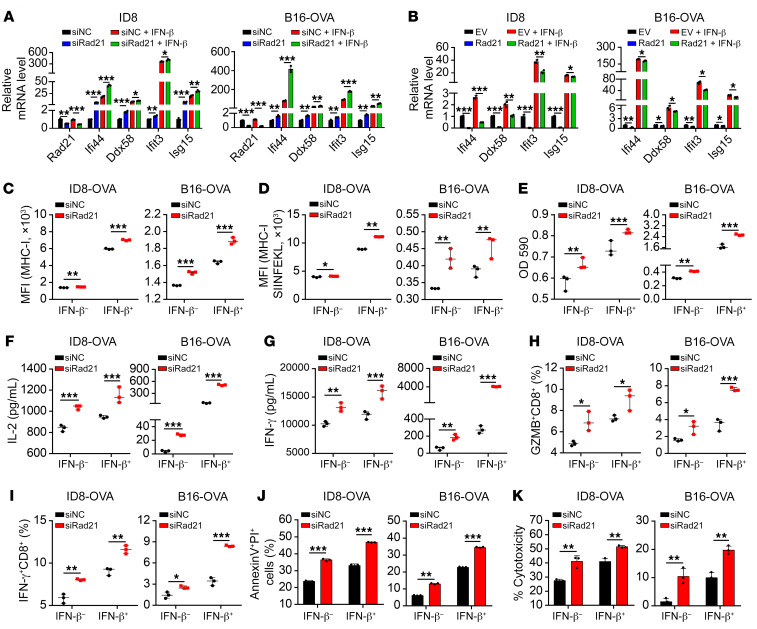
Figure 5. RAD21 ablation induces T cell activation in vitro.
(A and B) qRT-PCR validation of representative ISGs Ifi44, Ddx58, Ifit3, and Isg15 in Rad21-KD or Rad21-overexpressed and control ID8 cells and B16-OVA cells in the presence or absence of IFN-β treatment. (C and D) Expression levels of MHC-I and MHC-I–SIINFEKL on Rad21-KD and control ID8-OVA and B16-OVA cells in the presence or absence of IFN-β treatment were determined by FACS. (E–I) Rad21-KD and control ID8-OVA and B16-OVA cells were treated with vehicle or IFN-β and then cocultured with B3Z cells or OT-I cells, after which B3Z activation was determined by LacZ activity (E) and OT-I activation was determined by secretion of IL-2 (F) and IFN-γ (G) and expression of effector molecules GZMB (H) and IFN-γ (I). (J and K) The cytotoxic effect of OT-I was measured by annexin V/propidium iodide staining (J) and LDH release (K) of ID8-OVA and B16-OVA cells after coculture with OT-I for 48 hours. Data in A–K are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3, 2-tailed t test). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.