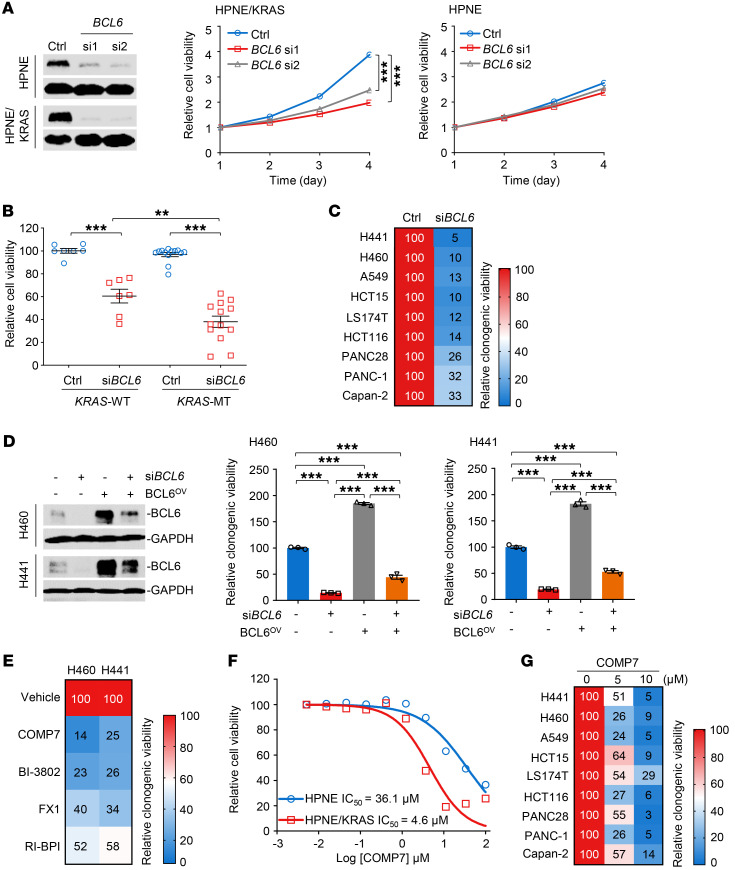
Figure 4. BCL6 inhibition impedes the growth of KRAS-mutant cancer cells in vitro.
(A) Effects of BCL6 knockdown on cell survival. The knockdown efficiency of siBCL6 was examined (left) and cell viability was measured using a Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) (right). Relative cell viability (normalized to day 0) is plotted. (B) BCL6 depletion led to selective cytotoxic effects toward KRAS-mutant cancer cell lines. Thirteen KRAS-mutant and 7 KRAS-WT cancer cell lines were transfected with siBCL6 or a scrambled siRNA control. Cell viability was measured 72 hours after transfection using a CCK-8 assay kit. Relative cell viability is shown by setting the untreated control as 100%. (C) The colony-formation ability of indicated cell lines after transfection with siBCL6 or siControl. The relative clonogenic viability is calculated by normalizing the untreated group as 100%. (D) Exogenous transduction of BCL6 (BCL6OV) reduced BCL6 knockdown–mediated cytotoxicity. BCL6 expression (left) and the relative cell viability of cultured colonies (right) are shown. (E) The colony-formation ability of indicated cell lines after treatment with BCL6i. The relative viability of cultured colonies is calculated by normalizing the untreated group as 100%. (F) The inhibitory effects of COMP7 on HPNE and HPNE/KRAS cells. Cells were treated with COMP7 at gradient concentrations for 72 hours. (G) COMP 7 suppressed the clonogenic growth of various KRAS-mutant cancer cell lines. Cells were treated with 5 μM or 10 μM COMP7 for 7 days. Data in A, B, D, and F are expressed as mean ± SEM of 3 technical replicates. Statistical analyses in A, B, and D were performed using 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. The immunoblots in A and D were contemporaneous and run in parallel from the same biological replicate, representative of at least 3 independent experiments.