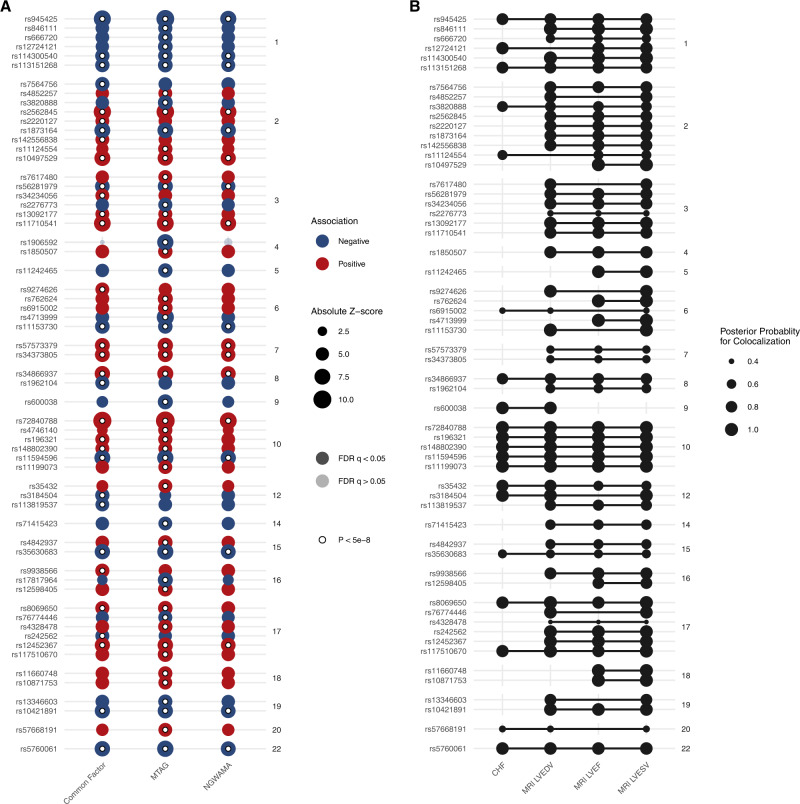
Fig. 5. Results of multivariate genome wide association study.
Multivariate GWAS and multi-trait colocalization were performed to identify genetic loci associated with HF and cardiac structure/function traits. A Results of multivariate GWAS. The x-axis denotes the multivariate GWAS method, and the y-axis denotes the independent lead variants at each locus. The size of each point denotes the absolute z-score for each trait. The shading of each point denotes whether the association met an FDR adjustment for multiple testing. Associations exceeding the conventional genome-wide significance threshold are denoted with a white circle. Variants are grouped by chromosome. B Results of multi-trait colocalization. The x-axis denotes heart failure and cardiac imaging traits. The y-axis represents the lead variant at each independent locus identified in the multivariate GWAS. Lines connect groups of traits with evidence of colocalization at a given locus. The size of each point represents the posterior probability for colocalization. Evidence for colocalization was determined based on the default variant specific regional and alignment priors , with colocalization identified when . FDR false discovery rate.