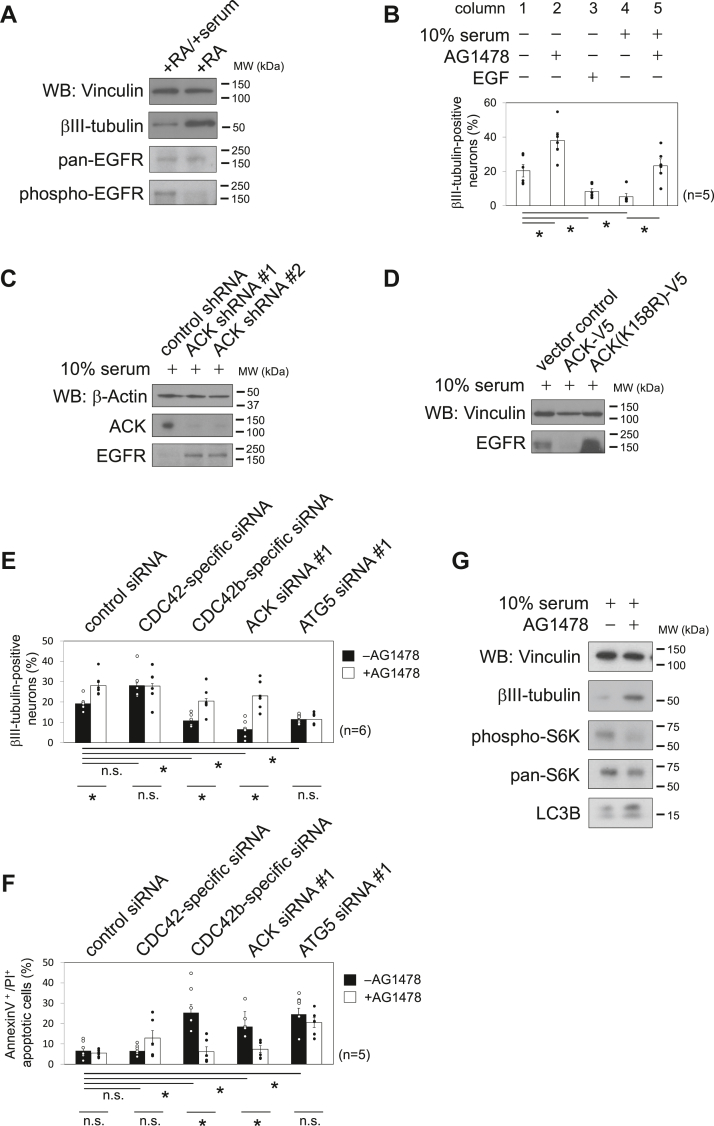
Figure 4.
Suppressing EGFR activity augments neural differentiation and autophagy.A, immunoblotting images showing the expression and phosphorylation levels of the indicated proteins. P19 cells were subjected to RA-induced neural protocol until day 6 and then cultured in 10% serum-containing αMEM (+RA/+serum) or B27-containing neurobasal media (+RA) until day 9. B, histograms showing the percentages of βIII-tubulin–positive neurons. P19 cells were subjected to RA-induced neural (−serum) or the neural progenitor cell (+10% serum) differentiation protocol in the presence or absence of AG1478 and EGF. Cells were fixed at day 9, and the numbers of βIII-tubulin–positive neurons were counted. Immunoblotting images showing the expression levels of the indicated proteins in ACK targeting shRNA-expressing (C) or ACK-V5-expressing cells (D). P19 cells were subjected to RA-induced neural progenitor cell differentiation. Histograms showing the percentages of βIII-tubulin–positive neurons (E) and apoptotic cells (F) upon treatment with siRNAs. Cells were subjected to transfection on day 5. Cells were fixed at day 9, and the numbers of βIII-tubulin–positive neurons or apoptotic cells were counted. Error bars indicate SEM (n = 5 in B, and n = 6 in E and F). Significance of differences is indicated by n.s. (not significant, p > 0.05) and ∗ (p < 0.05) using a Tukey’s test. G, immunoblotting images showing the expression and phosphorylation levels of the indicated proteins. P19 cells were subjected to the neural progenitor cell differentiation protocol in the presence or absence of AG1478. Cell lysates were collected at day 9. Black bars and numbers beside the panels indicate the positions and molecular sizes (kDa) of molecular markers. Vinculin (A, D, and G) or β-actin (C) served as loading controls. EGFR, EGF receptor; RA, retinoic acid.