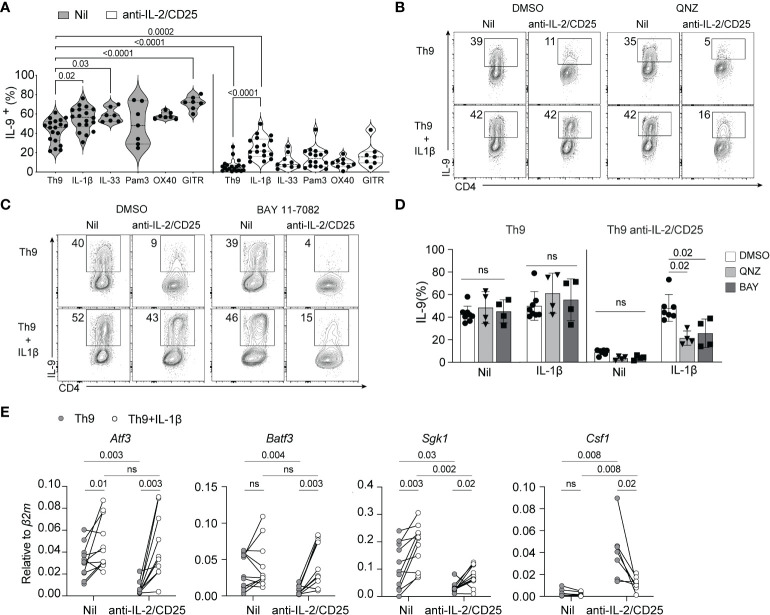
Figure 2.
IL-1β-induced NF-kB rescues Th9 differentiation in IL-2-limiting conditions. (A) Th9 cells were cultured in standard or IL-2-limiting conditions in the presence of the indicated NF-kB-activating cell surface receptors and cytokines, and intracellular IL-9 was measured at day 5 of culture after restimulation of cells with PMA and ionomycin. Each data point represents cells from at least n=7 mice or more per group. (B, C) Representative contour plots of IL-9 production of Th9 and IL-2-deprived Th9 cells in the presence or absence of IL-1β and the NF-kB inhibitors QNZ (1nm) or BAY 11-7082 (2.5μM), depicting the NF-kB-dependency of IL-1β-mediated rescue of Th9 cell differentiation. (D) Quantification of IL-9+ Th cells in culture with NF-kB inhibitors, each data point represents naïve T cell cultures from individual mice n= 4 mice from drug-treated cells and n=7 for DMSO controls. (E) NF-kB-associated gene expression at day 5 of culture from non-restimulated Th9 and IL-2-deprived Th9 cells cultured in the presence or absence of IL-1β. Each point represents data from T cells isolated from at least 8 or more mice per group. Data are considered significant if p value ≤0.05 in a one-way ANOVA analysis with a Tukey post-test. Error bars represent standard deviation. ns, non-significant.