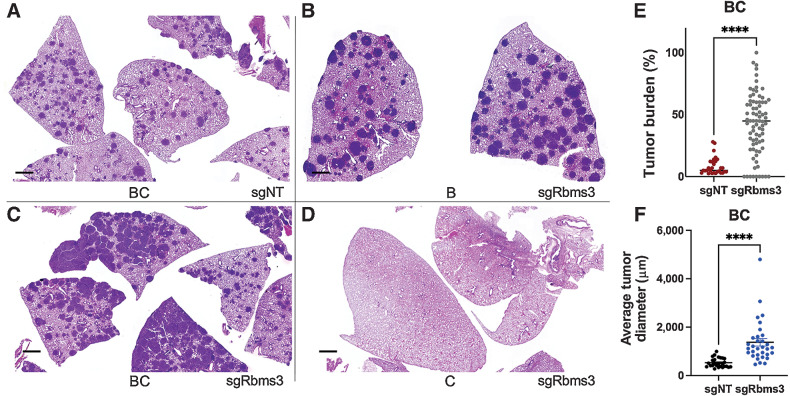
Figure 3.
CRISPR/Cas9 editing of Rbms3 cooperates with BRAFV600E in a mouse model of lung cancer. A–D, Representative images of different genotypes of harvested mouse lung sections following necropsy analyses stained with H&E 13 weeks after initiation with 5 × 104 pfu lenti-CRE. CRISPR/CAS9-mediated genome editing was used in panels A, C, and D to edit Rbms3 in vivo. Genotype and average tumor burden calculation of each experimental group was: A, sgNT-CRE virus in BrafCAT/+; H11LSL-CAS9 (BC) mice: 8.5%. B, sgRbms3-CRE virus in BrafCAT/+ (B) mice: 7.7%. C, sgRbms3-CRE virus in BC mice: 38.8%. D, sgRbms3-CRE virus in H11LSL-CAS9/+ (C) mice: 0%. Scale bar, 1,000 μm. E, Quantification of individual tumor burden from genotypes in A compared with C. Tumor-bearing lungs from B were identical to A. A paired t test was used to determine statistical significance; P < 0.01. F, Quantification of tumor diameter was performed in μm using 25 individual tumors from genotypes in A compared with C using the 3D Histech MIDI Slide Scanner QuantCenter. Comprehensive analyses was conducted with over 200 lung tumors. N = 50 mice individual or (biological replicates). N = 2 experimental replicates were performed comparing the indicated genotypes in A and C. Individual values are graphed, the black bar represents the mean. Error bars, SEM. A paired t test was used to determine statistical significance; ****, P < 0.0001.