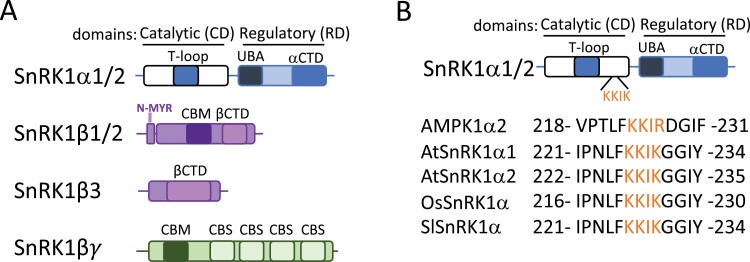
Fig. 1.
SnRK1 subunit architecture. (A) SnRK1α subunits contain a Ser/Thr kinase domain (referred to as the catalytic domain; CD) at the N-terminus followed by a regulatory domain (referred to as the RD) at the C-terminus. The CD contains an activation loop (T-loop), while the C-terminal part includes both ubiquitin-associated (UBA) and far C-terminal (αCTD) subdomains. The regulatory β-subunits consist of an N-terminal myristoylation (N-MYR) motif, a carbohydrate-binding module (CBM), and a β-C-terminal domain (βCTD) for SnRK1β1 and SnRK1β1, and a βCTD for SnRK1β3. The regulatory βγ-subunit combines four cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS) domains at the C-terminus with an N-terminal CBM. (B) Multiple amino acid sequence alignment of the putative nuclear localization signal (NLS) of SnRK1 from Arabidopsis thaliana (AtSnRK1α), Oryza sativa (OsSnRK1α), Solanum lycopersicum (SlSnRK1α) and human (AMPK1α2). The NLS is marked in orange.