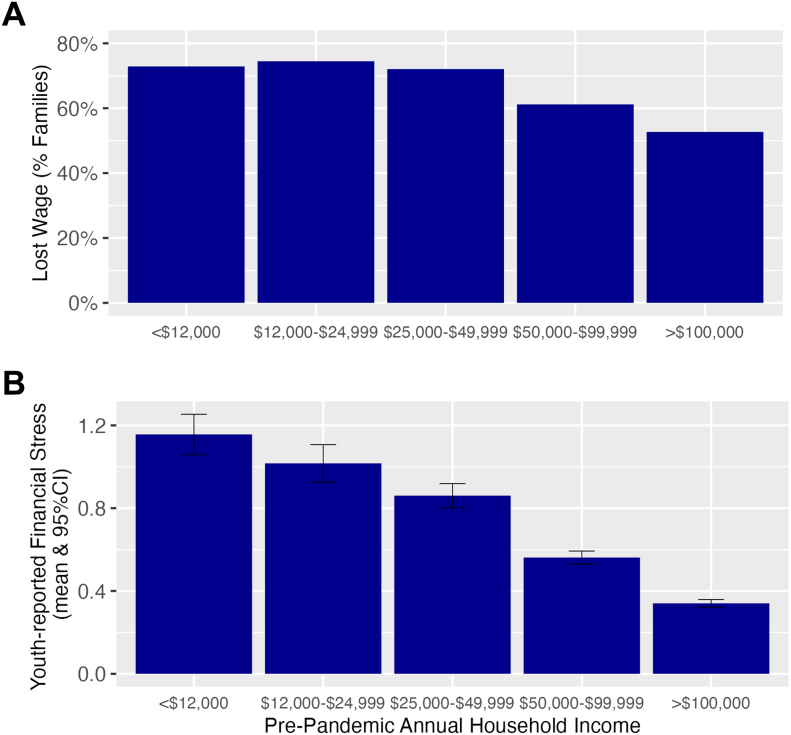
Fig. 1.
Household wage loss (A) and youth-reported financial stress (B) across quintiles of pre-pandemic annual household income. Pandemic-related financial strain was greater in lower income levels. (A) Experiencing wage loss during COVID-19 was less likely with higher pre-COVID annual income (logistic regression of pre-pandemic annual income level predicting income loss Odds ratio = 0.57, P < 0.001). (B) Youth financial stress (measured on a Likert scale from “never” [0] to “very frequently” [4] worrying that family will not have money to pay for necessities) during COVID-19 was lower with higher pre-COVID annual income (linear regression of income level predicting COVID-19 financial stress β = −0.339, P < 0.001).