Fig. 1.
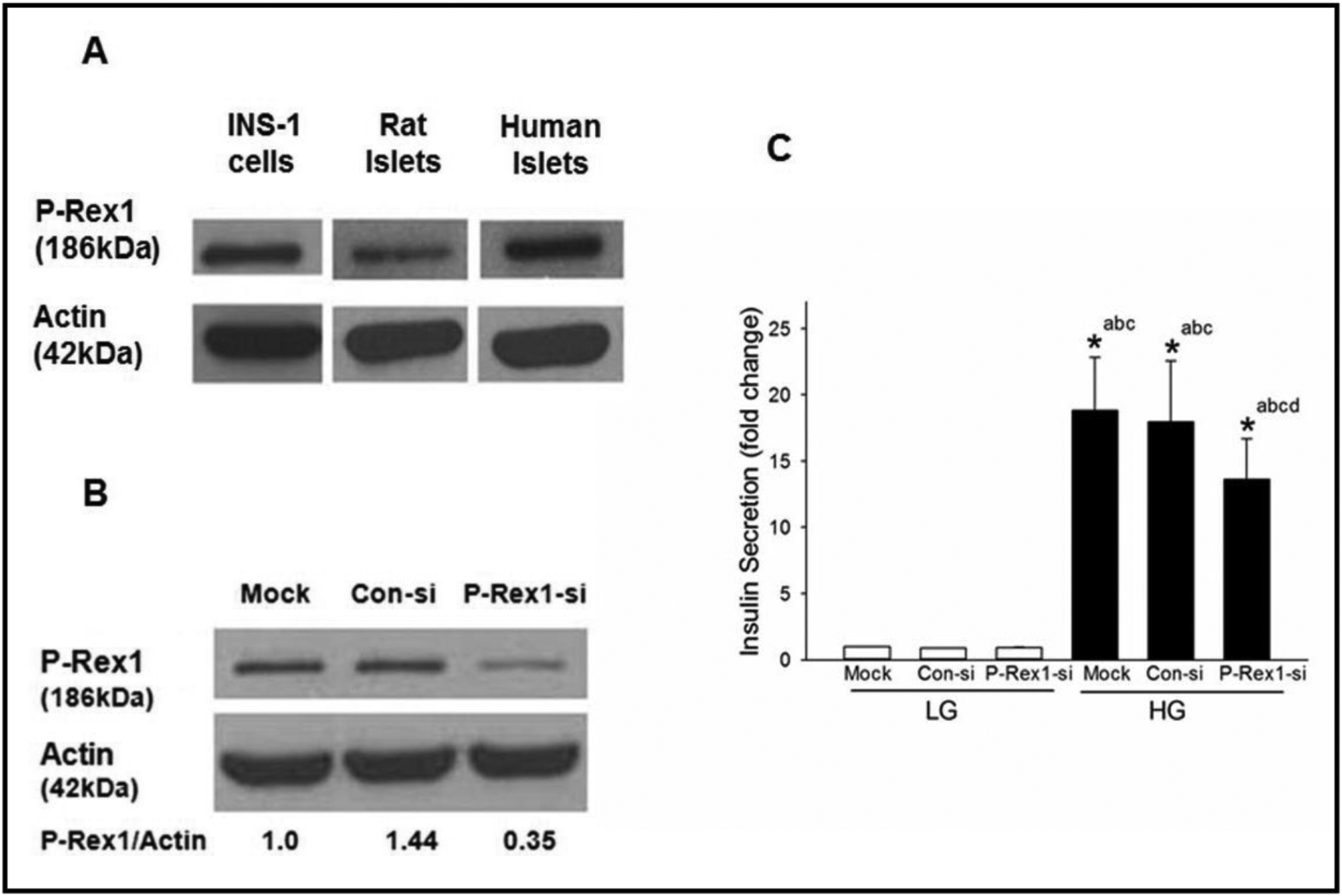
Expression of P-Rex1 in clonal INS-1 832/13 cells, rodent islets and human islets cells and siRNA mediated knockdown of P-Rex1 significantly attenuates GSIS in INS-1 832/13 cells. Panel A: Lysates from INS-1 832/13 cells, rat and human islets were analyzed for P-Rex1 protein expression by Western blot analysis. Actin was used as loading control. Panel B: INS-1 832/13 cells were transfected with Con-siRNA or siRNA targeted to P-Rex1 (P-Rex1-si). Cell lyates were analyzed by Western blotting for the expression of P-Rex1. Actin was used as loading control. A representative blot from three independent experiments is shown here. Panel C: GSIS was quantified in mock, Con-si and P-Rex1-si transfected INS-1 832/13 cells (see Methods for additional details). Data are mean ± SD from three experiments. The data are expressed as fold change relative to LG-Mock. (* p< 0.05) Comparisons shown: a -significant compared with LG treated mock; b - significant compared with LG-treated Con-si; c- significant compared with LG-treated P-Rex1-si; d: significant compared with HG-treated mock.
