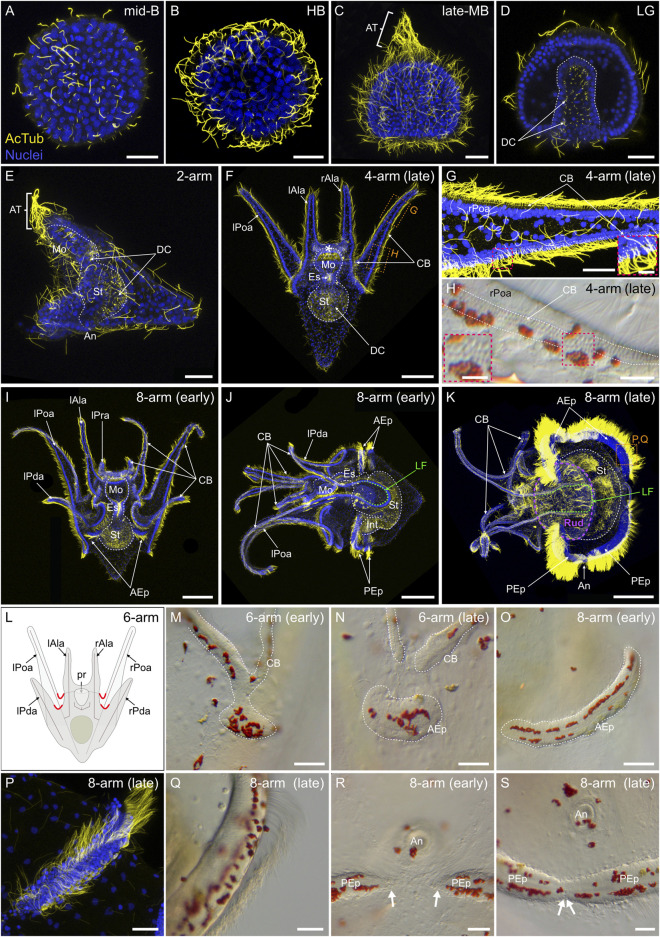
FIGURE 8.
Ciliogenesis in Paracentrotus lividus during the embryonic and larval periods. Developmental stages are as follows: (A) mid-blastula stage (mid-B); (B) hatched blastula stage (HB); (C) late mesenchyme blastula stage (late-MB); (D) late gastrula stage (LG); (E) 2-arm pluteus stage (2-arm); (F–H) 4-arm pluteus stage (4-arm); (I–K, O–S) 8-arm pluteus stage (8-arm); (L–N) 6-arm pluteus stage (6-arm). The use of (early) or (late) associated with the stage names simply highlights here more specific periods during the 4-, 6- or 8-arm pluteus stages. In (A–G,I–K,P), images are maximum intensity projections of confocal z-stacks of embryos and larvae co-labeled for acetylated α-tubulin (cilia; yellow) and DNA (nuclei; blue), and they correspond to projections of the entire specimen, except for (D) that is a cross-section through the embryo. In (H,M–O,Q–S), images were acquired using light microscopy. (L) Schematics of a larva at the 6-arm pluteus stage illustrating in red the areas of the ciliary band that will bud to form the epaulettes. In (A–D), embryos are in lateral view with the animal pole up. In (E,J,K), larvae are in left view, with the anterior side up and the ventral side left. In (F,I), larvae are in anterior view, with the ventral side up. (G,H) Close-ups of the ciliary band of a late 4-arm pluteus stage larva, corresponding to the regions outlined by orange boxes in (F). ((G) inset, (H) inset), Close-ups of the ciliary band to highlight the distribution of cuboidal cells and their associated cilia. (M–O) Close-ups of a ciliary band bud and its related epaulette during the 6- and 8-arm pluteus stages. (P,Q) Close-ups of the anterior epaulette in a larva at a late 8-arm pluteus stage, corresponding to the region outlined by the orange box in (K). (R,S) Close-ups of the posterior epaulettes in a larva at the begin and at the end of the 8-arm pluteus stage, respectively. In (D), the white dotted line outlines the archenteron and, in (E) (F), (I–K), the digestive tract. In (F), the white asterisk marks the oral hood. In (H), white dotted lines delineate the three rows of cuboidal cells and their associated cilia. In (J,K), the green dotted line indicates the position of the lateral field. In (K), the purple dotted line outlines the adult rudiment. In (M–O), the white dotted line highlights the ciliary band and the developing epaulette. In (R), white arrows mark the posterior end of the two posterior epaulettes and in (S) the site of fusion of the two posterior epaulettes. Scale bar: (A–E,G,M–N,P–S) 30 μm; (F) 50 μm; ((G) inset, (H) inset) 7.5 µm; (H) 15 μm; (I–K) 150 µm. AcTub: acetylated α-tubulin; AEp: anterior epaulette; An: anus; AT: apical tuft; CB: ciliary band; DC: digestive tract cilia; Es: esophagus; Int: intestine; lAla: left anterolateral arm; LF: lateral field; lPda: left posterodorsal arm; lPoa: left postoral arm; lPra: left preoral arm; Mo: mouth; PEp: posterior epaulette; pr: postoral region; rAla: right anterolateral arm; rPda: right posterodorsal arm; rPoa: right postoral arm; Rud: adult rudiment; St: stomach.