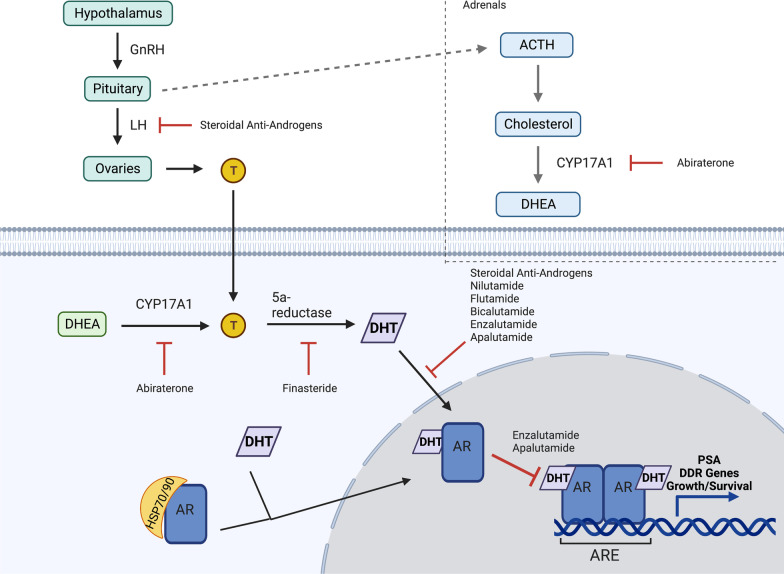
Fig. 1.
AR signalling pathways and therapeutic targets of AR. Androgens such as T are produced from cholesterol. CYP17A1 is the enzyme responsible for converting precursors to DHEA, and T is converted to DHT through 5a-reductase. DHT activates AR, resulting in its release from HSP70/90. AR then dimerizes and translocates to the nucleus where it can bind to AREs and modulate the transcription of target genes. Abiraterone irreversibly inhibits CYP17A1 activity. Bicalutamide and enzalutamide are AR antagonists that block the binding of DHT to AR. Enzalutamide also inhibits the nuclear translocation of AR. Abbreviations: GnRH—gonadotropin-releasing hormone, LH—luteinizing hormone, T—testosterone, ACTH—adrenocorticotropic hormone, DHEA—dehydroepiandrosterone, ARE—androgen response element, and PSA—prostate-specific antigen