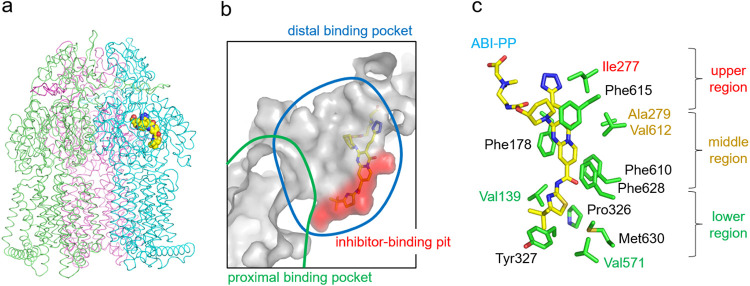
FIG 1.
Inhibitor-binding site of wild-type MexB. (a) Crystal structure of the inhibitor ABI-PP bound to the MexB trimer. Three MexB monomers are shown in green, blue, and red, representing the access, binding, and extrusion monomer, respectively. ABI-PP is shown as the yellow space-filling model. (b) Close-up view of the inhibitor-binding site. Substrate translocation pathway is shown as a solid gray surface. The proximal and distal binding pockets are indicated in green and blue circles, respectively. The inhibitor-binding pit is shown as a red surface. The ABI-PP molecule is represented as a yellow stick model. (c) Detailed inhibitor-binding site. Carbon atoms of ABI-PP and the amino acid residues are indicated in yellow and green, respectively. The classification of the amino acids is shown on the right side of the panel.