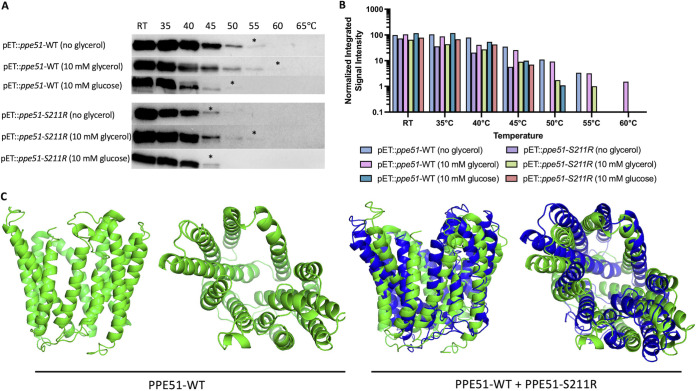
FIG 7.
Glycerol differentially interacts with recombinant WT PPE51 or S211R variant proteins. (A) Recombinant WT PPE51 and S211R proteins were assessed for thermostability under no glycerol, 10 mM glycerol, and 10 mM glucose conditions. The protein was preincubated at room temperature (RT) for 20 min and subjected to eight different temperature conditions as indicated for 5 min. Following heating, samples were spun down to pellet the protein precipitate. Soluble protein was removed and analyzed by immunoblotting. (*) represents the highest temperature where soluble protein was detected. (B) Signal intensity of individual bands were measured and normalized to the pET::ppe51-WT (no glycerol) band at RT. Samples containing glycerol continue to show detectable signal intensity up to 55°C for pET::ppe51-S211R and 60°C for pET::ppe51-WT. (C) in silico protein structure modeling and function prediction for PPE51. The peptide sequence of PPE51-WT (green) and PPE51-S211R (blue) were analyzed using the Iterative Threading ASSEmbly Refinement (I-TASSER) approach (51). Both WT and variant PPE51 were modeled without constraint and appear to form a porin-like structure with an inner channel. PPE51-S211R is modeled against the WT to show the slight conformational changes that occur with the introduction of this mutation. PPE51-WT and PPE51-S211R structures received C-scores of -0.86 and -1.24, respectively, which is a measure of structure confidence on a range of -5 (low) to 2 (high) (51). A model with C-score >-1.5 usually indicates a correct fold.