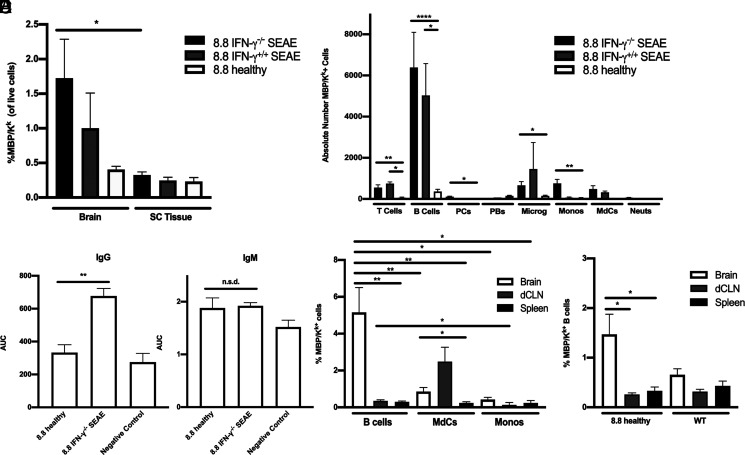
FIGURE 6.
B cells are the predominant cell type cross-presenting MBP in SEAE. (A, B, D, and E) Data obtained by flow cytometric analyses of mononuclear cells are shown as mean ± SEM. (A) The percentages of MBP/Kk+ cells are shown for the brain and spinal cord of 8.8 IFN-γ−/− (n = 21) and 8.8 IFN-γ+/+ (n = 4) mice with SEAE and age-matched 8.8 healthy mice (n = 14). (B) The numbers of MBP/Kk+ cells in the brains of 8.8 IFN-γ−/− (n = 14) and 8.8 IFN-γ+/+ (n = 2) mice with SEAE, and of age-matched 8.8 healthy mice (n = 8) are shown for the indicated cell types; gating strategy is shown in Supplemental Fig. 3C. (C) MBP-binding IgG and IgM Abs were detected in the serum of 8.8 IFN-γ−/− mice with SEAE (n = 25) and 8.8 healthy (n = 6) mice by ELISA; data are plotted as area under the curve (AUC). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) The percentages of MBP/Kk+ B cells, MdCs, and monocytes in the brain, deep cervical lymph node (dCLN), and spleen of 8.8 IFN-γ−/− SEAE mice (n = 16) are shown. (E) The percentages of MBP/Kk+ B cells in the brain, dCLN, and spleen of healthy 8.8 (n = 8) and WT mice (n = 7) are shown. Statistical significance was determined using a paired t test (A), Kruskal–Wallis with a Dunn’s posttest (B, E), Mann–Whitney U test (C), and two-way ANOVA with Šidák’s posttest (D). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.