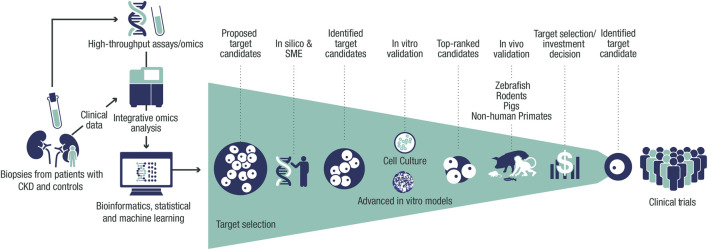
FIGURE 1.
Framework for target identification and validation in CKD. Potential CKD targets identified from human data via in silico and SME approaches are prioritized using thorough validation in vitro and in vivo systems, facilitating target selection. Target identification starts with the collection of biopsies, urine, and blood from patients with CKD and controls from clinical trials and collaborations. Omics data (genetic, transcriptomic, proteomic, and metabolomic) are then generated from these samples and processed with integrative omics analyses followed by bioinformatic and statistical analyses and machine learning. This data processing results in a list of CKD targets that is assessed in silico to build further evidence of human target–disease associations. The shortlisted targets are then prioritized by applying biologically relevant in vitro validation in cultured cells and advanced in vitro models. The targets with the strongest supportive data are then validated further in vivo to build proof-of-mechanism and proof-of-principle in CKD before being presented for target selection and investment decision to enter the portfolio. CKD, chronic kidney disease; SME, subject-matter expert.