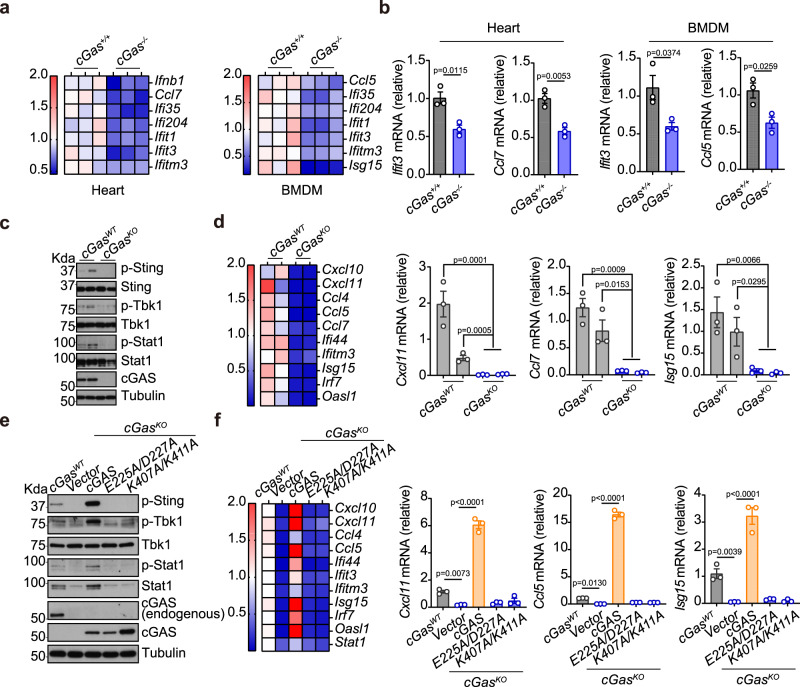
Fig. 5. cGAS drives STING signaling to maintain a basal state of immune defense.
a, b qRT-PCR analysis of baseline immune gene expression in cGASWT and cGASKO mouse heart or BMDMs (n = 3). Heatmaps of multiple ISGs are shown in a. Representative bar graphs are shown in b. c, d Western Blot (c) and qRT-PCR (d) analysis of tonic IFN signaling in cGASWT and cGASKO MEFs. Two independent clones of cGASWT and cGASKO MEFs were shown. p-Sting, p-Tbk1 and p-Stat1 are key phosphorylation events of the STING signaling pathway (c). Expression of ISGs are shown in a heatmap (d, left) and representative bar graphs (d, right). n = 3. e, f Western blot (c) and qRT-PCR (d) analysis of tonic IFN signaling in cGASWT and cGASKO MEFs reconstituted with vector control, wild-type cGAS, E225A/D227A cGAS (enzymatic-dead mutant), K407A/K411A cGAS (DNA-binding mutant). Cells were analyzed as in c, d. n = 3. Data are representative of at least three independent experiments. Data (b, d, and f) are shown as mean ± s.e.m. P values were determined by one-way ANOVA (b, d, and f).