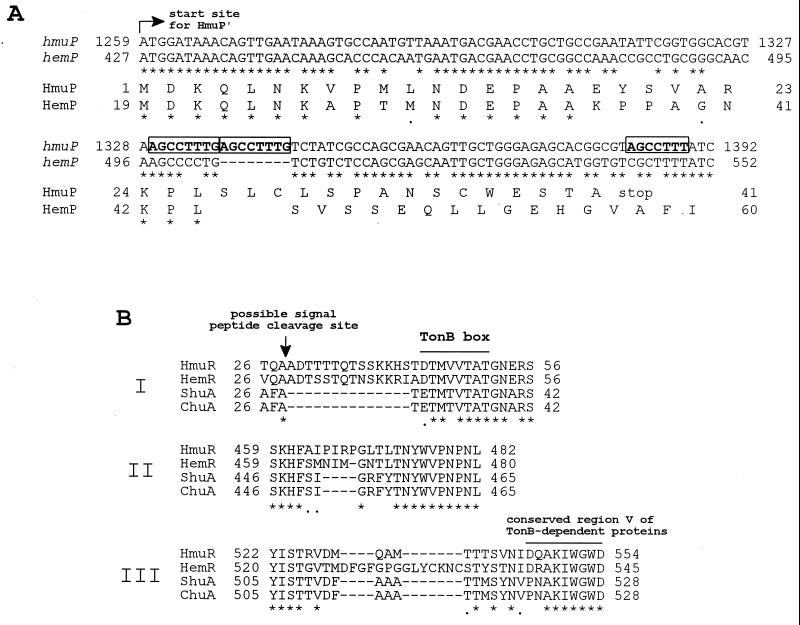
FIG. 2.
CLUSTAL W alignments of hmuP′ and HmuP′ sequences and selected HmuR sequences from Y. pestis with other homologous sequences. (A) Nucleotide and amino acid sequence comparisons of hmuP′ and the predicted translated gene product (HmuP′) of Y. pestis with hemP and HemP of Y. enterocolitica. Only the coding strands of hmuP′ and hemP are shown, and the translational start site for HmuP′ is indicated by the arrow. Repeated nucleotide sequences within hmuP′ are indicated by boldface letters in boxes. Conserved nucleotides or amino acids are indicated by asterisks. (B) Three regions (I, II, and III) of variability in hemin-uptake OM receptors from Y. pestis (HmuR), Y. enterocolitica (HemR), S. dysenteriae (ShuA), and E. coli O157:H7 (ChuA). The predicted signal peptide cleavage site for HmuR is indicated by the vertical arrow. The TonB box region and another conserved region (V) found to be associated with all TonB-dependent OM proteins are shown by overlines. Conserved amino acids are indicated by asterisks.