Abstract
The disease cancer is expanding on high spans in virtually all over the world, and undoubtedly, the research through all the aspects of sciences for each of its perspective is a great cause in reducing its severeness and symptoms. Chemotherapy is itself a cure to cancer as it helps in controlling the formation of cancerous cells but leaving multiple side effects on a human body. In this research work, we targeted 21 anticancer drugs that are in taken by the patients in combinations during chemotherapies. We introduce another branch of mathematics named as OR (Operations Research) linking to the chemical graph theory. Chemical graph theory allows us to generate highly resistant research on any structure via quantitative structure property relationship (QSPR) modeling to explore and develop new compounds for drugs. In this research study, we visualized what else the QSPR could provide when it comes to ranking drugs. We visualized the results obtained for boiling points and enthalpy of vaporizations through QSPR as the values of correlation coefficients and the errors generated under unique QSPR modeling. The implementation of VIKOR provides the best ranking for each of anticancer drugs when keeping in concern the specified properties, and the conclusions from this research work show another path to biologist scientists to create best combinations keeping in concern the study generated from QSPR.
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1140/epjp/s13360-022-03469-x.
Introduction
The phenomenal human body made up of blood and water is exceptionally functioning as mechanical models. It is composed of infinite many countable cells in each of its organ and running through the blood vessels. Each human body is adapted through genetics, and these genetics are working as a building block of generating human body from other bodies and keeping the genetic properties consistent. Cancer is highly observed through the background genes variations and formations. The six-alphabet word cancer is built up by the cause of abnormal sprout out of blood cells and their subdivisions at a high rate which measures the sharpness of it. It is irrespective of any measure of human age to lifestyle. The scientific advancements are in bloom to lessen the effects and severeness of it. It is a continuously ongoing development of harmful cells that even the removal of them cannot ensure it is again emergent anywhere in the human body. At certain and preferable levels, the chemotherapies are proposed for almost after every cancerous cell removal to avoid its certain increments. The chemotherapy, its link between cancer genetics is referred to [1, 2], is a treatment to cure cancer cells in which the combination of anticancer drugs is used to kill its cells. This research work leads to rank the highly effective anticancer drugs keeping in concern its properties.
A graph is an ordered pair with vertex set and edge set The degree (or valency) of a vertex is denoted as and is defined as the number of edges that are incident to it. We denote by the neighborhood degree of the vertex defined as the sum of degree of neighbors of a vertex in . By neighbors of a vertex, we mean the vertices adjacent to that vertex. For more basic theory of graphs, we are referring the reader to [3]. A simple graph, i.e., undirected connected graph with no multiple edges and no loops, having vertices and edges, is known as a molecular graph. Chemical graph theory [4] is the study of graphs considering each vertex as atom or molecule or a compound element, and each edge represents the bond between nodes of structure. QSPR (Quantitative Structure Property Relationship) [5] is a robust analytical approach for splitting down a molecule into a succession of numerical principles defined as chemical indices [6] each describing its properties. OR (Operations Research) [7] is a discipline that deals with development and application of advanced analytical methods to improve decision making by MCDM [8]. MCDM (Multi-Criteria Decision Making) is commendable field of OR (Operational Research). At a specific argument, the study of multiple intents through mathematical programming has arisen as an influential tool to access the best decisions. MCDM is about making decisions when multiple criteria (or objectives) need to be considered together to rank or choose between alternatives (here considering as drugs). MCDM concepts are used by researchers to optimize the process parameters in turning process. There are numerous MCDM approaches classified in many means, such as linear/nonlinear model and individualities of decision interplanetary. In this research work, we implement the highly compatible technique named as VIKOR. VIKOR was earlier recognized by Serafim Opricovic to interpret decision challenges with conflicting and non-commensurable (various elements) criteria, assuming that compromise is adequate for conflict determination, the decision-maker wants a solution that is the closest to the ideal, and the alternatives are evaluated according to all established criteria. In 1979, S. Opricovic had established the rudimentary concepts of VIKOR in his PhD dissertation, and an application was published in 1980 [9]. In 1990, the ideology of the word comprising five alphabets named VIKOR appeared in [10]. The VIKOR method was established for multi-criteria optimization of complex systems. It governs the compromise ranking list and the compromise solution obtained with the initial given weights. This technique focuses on ranking and selecting from a set of alternatives in the presence of conflicting criteria. In this research work, VIKOR method is optimizing the implementation of QSPR modeling to best rank the targeted drugs.
The raising research area aiding through chemical graph theory to formulate diversified compounds properties via chemical indices is escalating in the highest ratios. The research directed toward chemical graph theory is not only based on generating the finite numerical values for the compounds either covering biological sciences or solid physics, but also the new ideology implemented years ago which is constructed to read these descriptors and is through statistical modeling in order to obtain the relation; the correlation between each numerical descriptor and the properties corresponding to referred structure is defined as QSPR (Quantitative Structure Property Relationship). This involves certain evaluations generated through regression analysis keeping in concern the significance ability of the linked chemical index, its ability to predict specified properties with a unique correlation value and further the predicted values obtained from individual regression modeling. Undoubtedly, there is still a lot of vacancy for either already explored or unexplored compound area through this concept. The question in this research work is raised that QS (Quantitative Structural) analysis either for property, activity, or any chemically defined term to identify the uniqueness for specific compound is enough to identify and link certain categories of targeted compounds to obtain ideal compound or chem-formulae out of them. Here, we are going to introduce and establish another mathematical link to bio-chem graphical sciences via OR (Operations Research).
And this QSPR implementation ideology is introduced in detail in the following sections. This research concept is drawing toward certain mathematical and statistical evaluations implementations in MCDM technique named as VIKOR to rank anticancer drugs depending on criteria’s considering as chemical indices highly dependent on degree and the conclusions taken from QSPR analysis of 21 effective anticancer drugs used in chemotherapy performed by Shnamukha [11], in 2022. Highly resisted anticancer drugs, namely Alpelisib, Azacitidine, Cytarabine, Daunorubicin, Dexamethasone, Docetaxel, Doxorubicin, Glasdegib, Gilteritinib, Ivosidenib, Midostaurin, Olaparib, Paclitaxel, Palbociclib, Pamidronic acid, Prednisone, Ribociclib, Tioguanine, Toremifene, Tucatinib and Venetoclax as shown in Supporting Figures [S1–S21], respectively. Undoubtedly these drugs have severe hazardous conditions which prolongs for a lifetime depending on the human body ability to recover or completely not. Certain types of cancers [12] that observed to cure them by these drugs involve ovarian cancer, esophageal cancer, breast cancer, lung cancer, Kaposi’s sarcoma, cervical cancer, pancreatic cancer, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), acute lymphocytic leukemia (ALL) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) and many other from mild to severe.
Preliminaries
This section includes the history or recent works linked to QSPR analysis linking to chemical graph theory and MCDM techniques implementation in some real-life examples. This study motivates us to check the reliability to introduce another highly applicable branch named OR to the research era directing toward bio-chem sciences.
Ullah [13] performed evaluation on carbon nanosheets to draw comparative aspects between them. In 2022, Çolakoğlu [14] investigated the potential drug candidates against COVID-19 and performed certain mathematical modeling to discover new drugs through QSPR analysis. The detailed explanation and implementation of numerical values evaluated from topological indices and their usage in QSPR/ QSAR modeling to refine and predict their ability to correlate with referred physiochemical properties of corresponding bio-chem structure have been visualized by Dearden [15]. The role of chemical indices in drug discovery research in highly sprouting advancements and topological indices QSAR, the problem of 2D QSAR versus 3D QSAR, tactics of orthogonalization and the use of linear blend and semiempirical connectivity indices are also illustrated by Estrada [6]. The numerous research area linking chemical graph theory and cheminformatics has been investigated via QSPR modeling by Ivanciuc [16]. Opricovic [17] performed comparative analysis of TOPSIS and VIKOR. Kumar [18] drawn optimal rankings toward sustainable renewable energy development using MCDM. Geographical information system and MCDM methods have been implemented by Sánchez-Lozano [19], for the evaluations of solar farms locations.
Materials and methods
Data analysis tool of Microsoft excel is used to obtain results generated from QSPR modeling via regression analysis. All the data in charts and tables evaluated for VIKOR technique are computed in Microsoft excel.
Environment to extract and implement QSPR conclusions into VIKOR
The motivation here is taken through the concept how multiple drugs (structures) are distinguished, and their dominance can be ranked when they get investigated for multiple criteria’s keeping in concern as chemical indices. The QSPR modeling has been performed for 11 chemical indices, namely first Zagreb index , second Zagreb index [20], atom bond connectivity index [21], inverse sum deg index IS(D) [22], symmetric division deg index SS(D) [23], Sombor index SO(D) [24], augmented Zagreb index A(D) [25], Randić index R(D) [26], reduced reciprocal Zagreb index RR(D) [27], harmonic index H(D) [28] and forgotten index F(D) [29].
Drugs are strongly classified by their physio-compound properties. In this research work, we are extracting QSPR for melting and boiling points. In order to distinguish drugs. We have developed some research on drugs that the more soluble the drug is, the more effective its intake becomes. Many substances are endothermic which affect the process of dissolution by absorbing heat in high entities. Thus, various drug studies show that lower the melting point, greater the drug positive effect and same for boiling points. High boiling points ultimately reach to eruption or evaporation that leave the drugs with its lower impacts for the targeted disease and that directed toward the values enthalpy of vaporization, here keeping in concern as 21 anticancer drugs used in chemotherapy as mentioned in introduction. Predicting physical properties like melting/boiling points, enthalpy of vaporization, etc., is very important for medicinal and environmental chemistry. These physical parameters are very important to estimate the solubility of chemical compounds. There is great amount of research done yet by Tetko on how accurately these physicochemical properties can be predicted [30] and relationship between drug absorption and melting point [31]. Chu et al. [32] performed QSPR study for breast cancer drugs. Fix et al. [33] performed research on resistant cancer cells by targeting low boiling point phase change ultrasound contrast agents. Rojas et al. [34] used low boiling point phase change contrast agents for vivo molecular imaging. We aim to observe the conclusions derived from QSPR analysis under the two physio-compound properties named as BP (boiling point) and EV (enthalpy of vaporization).
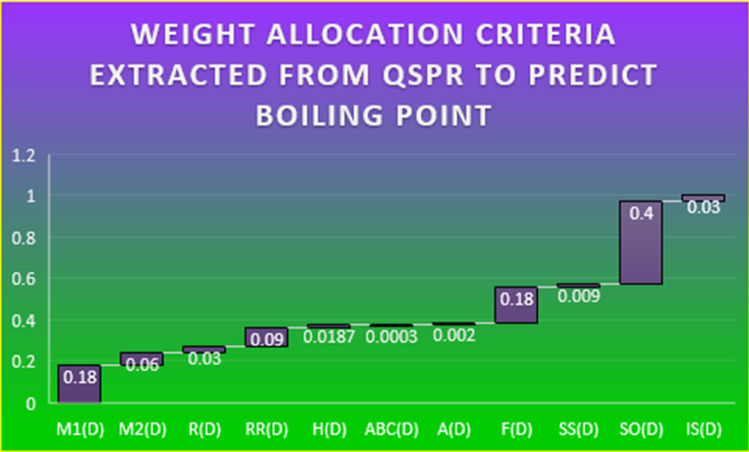
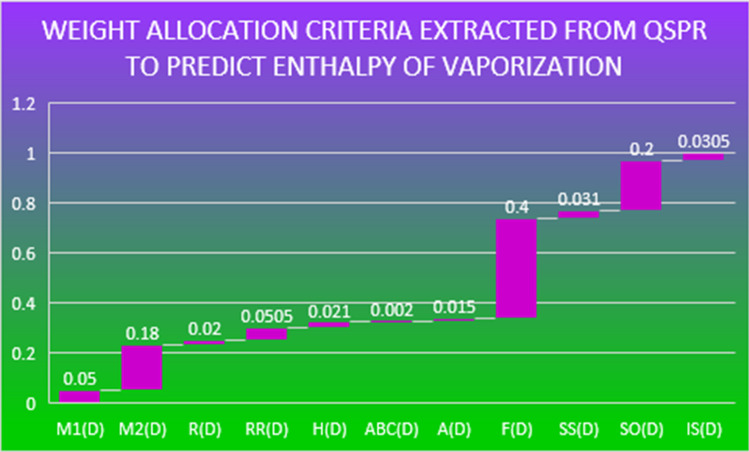
Next, we have considered the important results obtained from QSPR modeling from [11]. Particularly, we are considering here regression correlation coefficients and standard error (SE) values between the properties (BP and EV) and all chemical indices to observe in detail each numerical entity representing some correlation value as shown in Table 1. The closer the value of to 1 and low standard error show the good correlation ability of corresponding chemical indices to predict targeted properties. This concept indicates that the targeted considered outputs ( and SE) we have considered from QSPR show that both play great role to understand the ability of targeted chemical indices to predict targeted drugs physicochemical properties. Furthermore, the highly statistical-based obtained conclusions and their predicting ability observed in a numerical form as shown in Table 1 allow us to rank the targeted anticancer drugs under the criteria environment based on QSPR.
Table 1.
Regression correlation coefficient and standard error (SE) between each physical property and anticancer drugs
| (SE) | (SE) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.895 | 67.479 | 0.845 | 10.806 | |
| 0.887 | 69.857 | 0.849 | 10.656 | |
| 0.885 | 70.225 | 0.812 | 11.79 | |
| 0.89 | 68.933 | 0.833 | 11.164 | |
| 0.873 | 73.545 | 0.793 | 12.307 | |
| 0.823 | 85.675 | 0.729 | 13.807 | |
| 0.87 | 74.567 | 0.799 | 12.133 | |
| 0.895 | 67.500 | 0.876 | 9.717 | |
| 0.878 | 72.214 | 0.814 | 11.721 | |
| 0.898 | 64.403 | 0.854 | 10.501 | |
| 0.885 | 70.318 | 0.822 | 11.479 | |
From Table 1, we will dictate correlation coefficient as weight allocation criteria for boiling point case in Fig. 1 and for enthalpy of vaporization case in Fig. 2 and standard error as beneficial and non-beneficial criteria for both cases shown in Table 2 corresponding to each drug and its chemical indices. Benefical criteria are choosen for numerical values that are bold.
Fig. 1.
Weight allocation from QSPR extractions for boiling point
Fig. 2.
Weight allocation from QSPR extractions for enthalpy of vaporization
Table 2.
Beneficial and non-beneficial criteria for BP and EV
| Chemical indices | BP | EV |
|---|---|---|
| 67.479 | 10.806 | |
| 69.857 | 10.656 | |
| 70.225 | 11.79 | |
| 68.933 | 11.164 | |
| 73.545 | 12.307 | |
| 85.675 | 13.807 | |
| 74.567 | 12.133 | |
| 67.5 | 9.717 | |
| 72.214 | 11.721 | |
| 64.403 | 10.501 | |
| 70.318 | 11.479 |
Methodology for VIKOR and its implementation
To attain the adjacent finest result to the decisive, we contrivance VIKOR, where the anticancer drugs considering as alternatives, is appraised according to the established criteria’s which we considered under the case study for the observations generating QSPR. VIKOR ranks anticancer drugs and governs the solution named compromise that is nearest to the ultimate. Zeleny [35] and Yu [36], in 1973, presented the philosophy of compromise solution in MCDM. Its real applications were presented in 1998 [37].
The proposed technique comprised of the following steps:
- Determination of ideal best and ideal worst values where for all criterion functions which we considered as predicted properties.
- Determination of the values of (weighted normalized Manhattan distance) and (weighted normalized Chebyshev distance) where . We have the following inequalities.
-
Determination of values , through the following equality
whereas is the weight of the individual regret. This strategy could be compromised by .
Rank the alternatives, sorting by the values and from the minimum value.
VIKOR evaluations for BP QSPR extractions
In case for extracting results depending on correlation value and errors from QSPR analysis under the study of BP, we have obtained the following steps calculations for step 1 in Supporting Table S1, step 2 in Supporting Table S2 and final calculations for steps 2, 3 and 4 in Table 3.
Table 3.
Outputs for and rank (BP case)
| Anticancer drugs | BP QSPR VIKOR rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpelisib | 0.577194 | 0.245993 | 0.580896 | 13 |
| Azacitidine | 0.763794 | 0.348169 | 0.862527 | 18 |
| Cytarabine | 0.772701 | 0.35365 | 0.876849 | 19 |
| Daunorubicin | 0.449734 | 0.172333 | 0.382896 | 7 |
| Dexamethasone | 0.580471 | 0.249917 | 0.588943 | 14 |
| Docetaxel | 0.181172 | 0.056501 | 0.023011 | 3 |
| Doxorubicin | 0.440856 | 0.167141 | 0.369015 | 6 |
| Glasdegib | 0.638289 | 0.275422 | 0.667248 | 16 |
| Gilteritinib | 0.483351 | 0.184578 | 0.424662 | 8 |
| Ivosidenib | 0.431445 | 0.159721 | 0.35151 | 5 |
| Midostaurin | 0.337441 | 0.112607 | 0.215977 | 4 |
| Olaparib | 0.561948 | 0.232056 | 0.549752 | 11 |
| Paclitaxel | 0.148864 | 0.06 | 0.005093 | 1 |
| Palbociclib | 0.553575 | 0.226845 | 0.536202 | 10 |
| Pamidronic acid | 0.814134 | 0.381662 | 0.947135 | 20 |
| Prednisone | 0.606037 | 0.26486 | 0.628902 | 15 |
| Ribociclib | 0.569449 | 0.235444 | 0.560025 | 12 |
| Tioguanine | 0.850882 | 0.4 | 1 | 21 |
| Toremifene | 0.652638 | 0.280399 | 0.684712 | 17 |
| Tucatinib | 0.493892 | 0.194113 | 0.44605 | 9 |
| Venetoclax | 0.169572 | 0.057026 | 0.015513 | 2 |
| 0.148864 | 0.056501 | |||
| 0.850882 | 0.4 |
VIKOR evaluations for EV QSPR extractions
In case for extracting results depending on correlation value and errors from QSPR analysis under the study of EV, we have obtained the following steps calculations for step 1 in Supporting Table S3, step 2 in Supporting Table S4 and final calculations for steps 2, 3 and 4 in Table 4.
Table 4.
Outputs for and rank (EV case)
| Anticancer drugs | EV QSPR VIKOR rank | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alpelisib | 0.565214 | 0.243236 | 0.588969 | 14 |
| Azacitidine | 0.713466 | 0.353477 | 0.874597 | 18 |
| Cytarabine | 0.7192 | 0.357522 | 0.885335 | 19 |
| Daunorubicin | 0.447335 | 0.169406 | 0.381419 | 7 |
| Dexamethasone | 0.538918 | 0.233123 | 0.551663 | 10 |
| Docetaxel | 0.222318 | 0.046624 | 0.010915 | 2 |
| Doxorubicin | 0.441535 | 0.16536 | 0.370623 | 5 |
| Glasdegib | 0.62183 | 0.289254 | 0.703591 | 16 |
| Gilteritinib | 0.505865 | 0.206827 | 0.485551 | 9 |
| Ivosidenib | 0.44394 | 0.166372 | 0.374157 | 6 |
| Midostaurin | 0.345751 | 0.099621 | 0.193843 | 4 |
| Olaparib | 0.558119 | 0.245259 | 0.585626 | 12 |
| Paclitaxel | 0.209837 | 0.0505 | 0.005484 | 1 |
| Palbociclib | 0.55258 | 0.241214 | 0.575058 | 11 |
| Pamidronic acid | 0.735507 | 0.366625 | 0.912475 | 20 |
| Prednisone | 0.557713 | 0.247788 | 0.588849 | 13 |
| Ribociclib | 0.568689 | 0.251327 | 0.603456 | 15 |
| Tioguanine | 0.781592 | 0.4 | 1 | 21 |
| Toremifene | 0.643363 | 0.301896 | 0.740309 | 17 |
| Tucatinib | 0.504656 | 0.206827 | 0.484494 | 8 |
| Venetoclax | 0.25069 | 0.050009 | 0.040515 | 3 |
| 0.209837 | 0.046624 | |||
| 0.781592 | 0.4 |
Conclusion
The targeted 21 anticancer drugs that are used in combinations during chemotherapies have been observed under the highly applicable technique of MCDM named as VIKOR, and the background setting for VIKOR is exceedingly dependent on the evaluations and has been observed under the QSPR modeling by keeping in concern two properties named as boiling point and enthalpy of vaporization. This idea is applied for the drug study where these two properties cause high effects in the intake of these drugs. The values we considered from QSPR are the correlation coefficients that come under the relation between each individual property and all the targeted degree-based chemical indices and the values of errors generated under QSPR evaluations. The reason to use inputs from degree-based chemical indices is that they show high significance which glorifies the ability for each index to predict specified property. As we already overcome with the problems of choosing and estimating best chemical compounds that forms drugs to create other and modern drugs, the point what is next to QSPR is the motivation in this research work which shows that having multiple drugs and their usage in same disease, how we can create their combinations depending on the chemical indices study, keeping in concern highly noticeable properties for the drugs created for life in cancer. We have performed certain evaluations through the decision-making technique keeping in concern this new motivation, and the rank obtained from both BP and EV is shown in Fig. 3, which clarifies the ranking for 21 concerned drugs and generates vastly noticeable results for the scientists and chemists to form their highly achievable results when used in combination, and from the obtained ranking, we have eight out of 21 anticancer drugs that obtained the same ranking in both the process of VIKOR running under observations applied from both boiling points (BP) and enthalpy of vaporization (EV); their names and rankings are as follows: Midostaurin (Rank 4), Daunorubicin (Rank 7), Glasdegib (Rank 16), Toremifene (Rank 17), Azacitidine (Rank 18), Cytarabine (Rank 19), Pamidronic acid (Rank 20) and Tioguanine (Rank 21) which lead us to the conclusion for keeping in concern both properties (BP and EV) each evaluation under VIKOR rank eight anticancer drugs equivalent. Furthermore, this ideology sets new era that will be beneficial to rank any area of structures either linked to chem-bio or physics sciences when chemical indices create a high call via QSPR for the targeted properties and to visualize how the evaluations obtained from QSPR effect the rank ordering when dealing with multiple structures and under multiple criteria. Keeping in note that the concern is not only chemical indices, but also at what chemical cost individual targeted chemical index contributes to obtain the best structure which we visualized by considering the values obtained from correlation coefficients and errors generated under QSPR modeling.
Fig. 3.
Ranking 21 anticancer drugs under the study of QSPR modeling for degree-based chemical indices via decision-making technique VIKOR keeping in concern their values for boiling points (BP) and enthalpy of vaporization (EV)
Supporting information
Additional supporting information that includes supporting tables and figures is available in the supporting information file attached with the manuscript.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Funding
None.
Data Availability Statement
The results of this study are available only within the paper to support the data.
Declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors announce that no conflict of interest exists.
Contributor Information
Yali Li, Email: liyali@pdsu.edu.cn.
Adnan Aslam, Email: adnanaslam15@yahoo.com.
Saadia Saeed, Email: syyeda221@gmail.com.
Guoping Zhang, Email: zhangguoping@pdsu.edu.cn.
Salma Kanwal, Email: salma.kanwal@lcwu.edu.pk.
References
- 1.Alfarouk KO, Stock CM, Taylor S, Walsh M, Muddathir AK, Verduzco D, et al. Resistance to cancer chemotherapy: failure in drug response from ADME to P-gp. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0221-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Johnstone RW, Ruefli AA, Lowe SW. Apoptosis: a link between cancer genetics and chemotherapy. Cell. 2002;108(2):153–164. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.West DB. Introduction to graph theory. Upper Saddle River: Prentice hall; 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Trinajstić N. Chemical graph theory. Boca Raton: CRC Press; 2018. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Katritzky AR, Lobanov VS, Karelson M. QSPR: the correlation and quantitative prediction of chemical and physical properties from structure. Chem. Soc. Rev. 1995;24(4):279–287. doi: 10.1039/cs9952400279. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Estrada E, Uriarte E. Recent advances on the role of topological indices in drug discovery research. Curr. Med. Chem. 2001;8(13):1573–1588. doi: 10.2174/0929867013371923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.C. Churchman, R. Ackoff, E. Arnoff, Introduction to operations research. John Wiley and Sons Inc., New York (1957)
- 8.Edwards W. The theory of decision making. Psychol. Bull. 1954;51(4):380. doi: 10.1037/h0053870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Duckstein L, Opricovic S. Multiobjective optimization in river basin development. Water Resour. Res. 1980;16(1):14–20. doi: 10.1029/WR016i001p00014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 10.S. Opricovic, Programskipaket VIKOR zavisekriterijumskokompromisnorangiranje, in 17th International symposium on operational research SYM-OP-IS. (1990, October)
- 11.Shanmukha MC, Usha A, Praveen BM, Douhadji A. Degree-based molecular descriptors and QSPR analysis of breast cancer drugs. J. Math. 2022;2022:1–13. doi: 10.1155/2022/5880011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 12.The American Society of Health-System Pharmacist. Archived from the original on September 14, 2017. Accessed 2 Jan 2015
- 13.Ullah A, Qasim M, Zaman S, Khan A. Computational and comparative aspects of two carbon nanosheets with respect to some novel topological indices. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022;13(4):101672. doi: 10.1016/j.asej.2021.101672. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Çolakoğlu Ö. QSPR modeling with topological indices of some potential drug candidates against COVID-19. J. Math. 2022;2022:1–9. doi: 10.1155/2022/3785932. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.J. C. Dearden, The use of topological indices in QSAR and QSPR modeling, in Advances in QSAR modeling (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp. 57–88
- 16.Ivanciuc O. Chemical graphs, molecular matrices and topological indices in chemoinformatics and quantitative structure-activity relationships §. Curr. Comput. Aided Drug Des. 2013;9(2):153–163. doi: 10.2174/1573409911309020002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Opricovic S, Tzeng GH. Compromise solution by MCDM methods: a comparative analysis of VIKOR and TOPSIS. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2004;156(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/S0377-2217(03)00020-1. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kumar A, Sah B, Singh AR, Deng Y, He X, Kumar P, Bansal RC. A review of multi criteria decision making (MCDM) towards sustainable renewable energy development. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2017;69:596–609. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.191. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sánchez-Lozano JM, Teruel-Solano J, Soto-Elvira PL, García-Cascales MS. Geographical information systems (GIS) and multi-criteria decision making (MCDM) methods for the evaluation of solar farms locations: case study in south-eastern Spain. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013;24:544–556. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2013.03.019. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.I. Gutman, B. Ru?? Ić, N. Trinajstić, C. F. Wilcox Jr, Graph theory and molecular orbitals. XII. Acyclic polyenes. J. Chem. Phys., 62(9), 3399-3405 (1975)
- 21.E. Estrada, L. Torres, L. Rodriguez, I. Gutman, An atom-bond connectivity index: modelling the enthalpy of formation of alkanes (1998)
- 22.Vukičević D, Gašperov M. Bond additive modeling 1. Adriatic indices. Croaticachemicaacta. 2010;83(3):243–260. [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhao W, Shanmukha MC, Usha A, Farahani MR, Shilpa KC. Computing SS index of certain dendrimers. J. Math. 2021;2021:1–14. [Google Scholar]
- 24.Gutman I. Geometric approach to degree-based topological indices: sombor indices. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2021;86(1):11–16. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Furtula B, Graovac A, Vukičević D. Augmented zagreb index. J. Math. Chem. 2010;48(2):370–380. doi: 10.1007/s10910-010-9677-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Randic M. Characterization of molecular branching. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1975;97(23):6609–6615. doi: 10.1021/ja00856a001. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Gutman I, Furtula B, Elphick C. Three new/old vertex-degree-based topological indices. MATCH Commun. Math. Comput. Chem. 2014;72(3):617–632. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Fajtlowicz S. On conjectures of Graffiti-II. Congr. Numer. 1987;60:187–197. [Google Scholar]
- 29.Furtula B, Gutman I. A forgotton topological index. J. Math. Chem. 2015;53:213–220. doi: 10.1007/s10910-015-0480-z. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tetko IV, Sushko Y, Novotarskyi S, Patiny L, Kondratov I, Petrenko AE, Asiri AM. How accurately can we predict the melting points of drug-like compounds? J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014;54(12):3320–3329. doi: 10.1021/ci5005288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Chu KA, Yalkowsky SH. An interesting relationship between drug absorption and melting point. Int. J. Pharm. 2009;373(1–2):24–40. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.01.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.A. Rauf, M. Naeem, J. Rahman, A. V. Saleem, QSPR study of Ve-degree based end Vertice edge entropy indices with physio-chemical properties of breast cancer drugs. Polycycl. Aromat. Compd., 1–14 (2022)
- 33.S. M. Fix, A. Novell, J. M. Escoffre, J. K. Tsuruta, P. A. Dayton, A. Bouakaz, In-vitro delivery of BLM into resistant cancer cell line using sonoporation with low-boiling point phase change ultrasound contrast agents, in 2017 IEEE International Ultrasonics Symposium (IUS) (pp. 1–4). IEEE (2017, September)
- 34.Rojas JD, Dayton PA. In vivo molecular imaging using low-boiling-point phase-change contrast agents: a proof of concept study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2019;45(1):177–191. doi: 10.1016/j.ultrasmedbio.2018.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.M. Zeleny, Compromise programming. Multiple Criteria Dec. Mak. (1973)
- 36.Yu PL. A class of solutions for group decision problems. Manage. Sci. 1973;19(8):936–946. doi: 10.1287/mnsc.19.8.936. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.SerafimOpricovic, Multicriteria optimization in civil engineering (in Serbian), Faculty of Civil Engineering, Belgrade, 302 p (1998)
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The results of this study are available only within the paper to support the data.