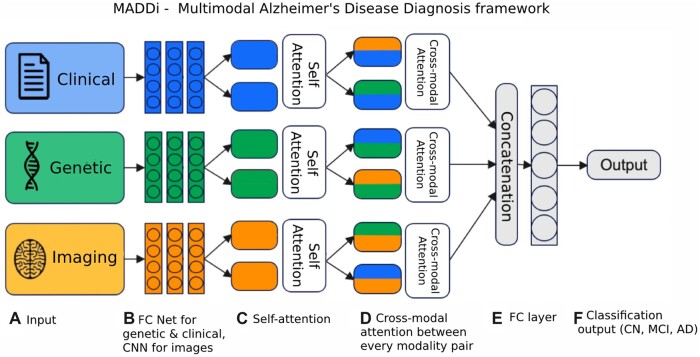
Figure 2.
Model architecture. (A) Data inputs—clinical data (demographics, memory tests, balance score, etc.), genetic (SNPs), and imaging (MRI scans). (B) The input sources are combined and fed into a fully connected (FC) neural network architecture for genetic and clinical modalities and a convolutional neural network (CNN) for imaging data. (C) Using the obtained features from the neural networks, a self-attention layer reinforces any inner-modal connections. (D) Then, each modality pair is fed to a bi-directional cross-modal attention layer which captures the interactions between modalities. (E) Finally, the outputs are concatenated and passed into a decision layer for classification into the (F) output Alzheimer’s stages (CN, MCI, and AD).