Figure 2: Effects of increased Pi availability on cellular signaling.
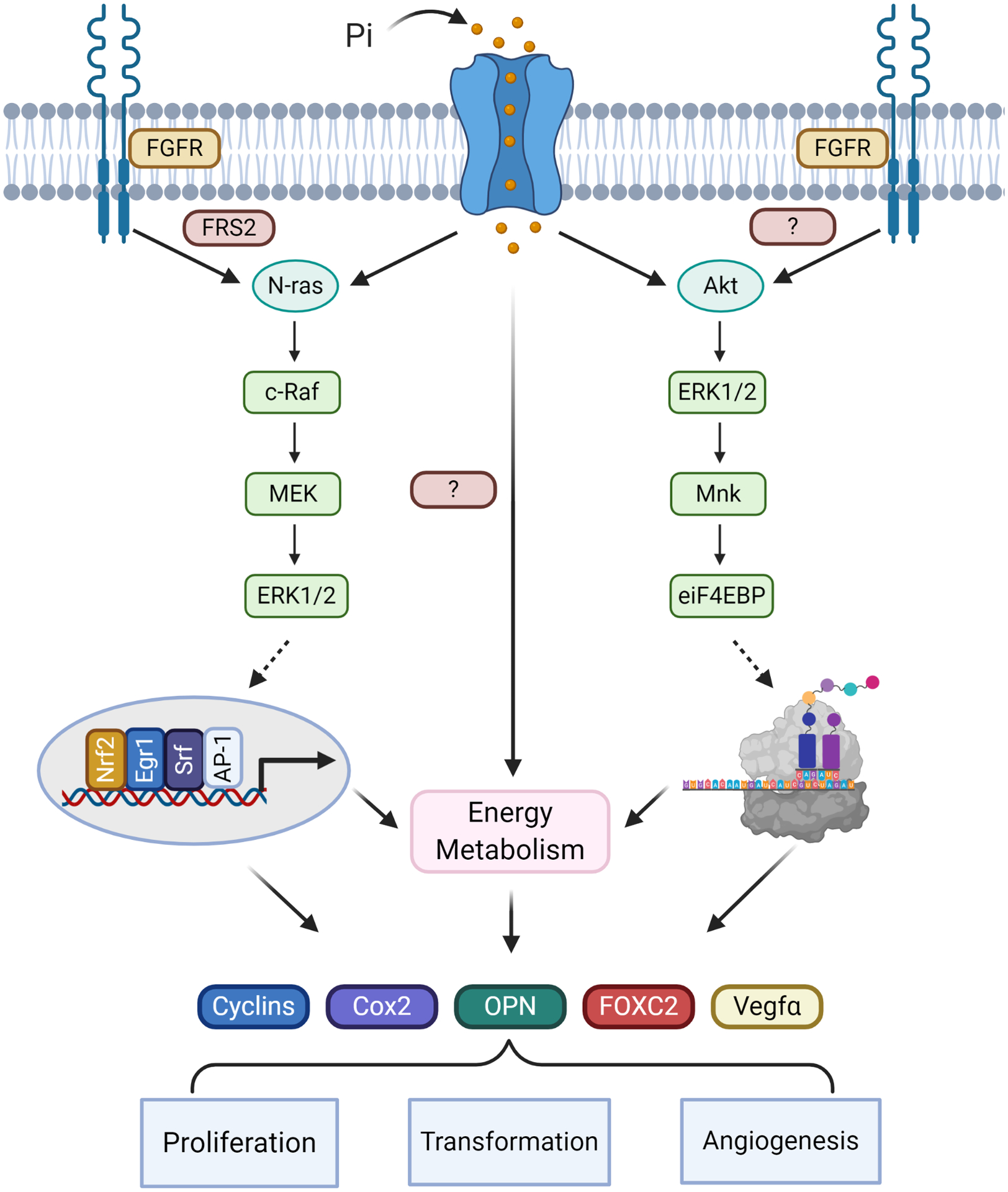
Cell-based studies have identified specific membrane and signaling events associated with increased extracellular Pi availability including the coordinated requirement of sodium dependent Pi-transporters/sensors as well as FGF receptor signaling. Downstream signaling proteins include the FGF receptor associated factor FRS2, as well as N-ras, c-raf, Mek and ERK1/2, leading to activation of transcription factors such as AP-1, Srf, Nrf2, and Egr-1 and expression of genes associated with cell growth and metabolism. A second pathway identified as Pi-responsive includes Akt, ERK1/2, Mnk ultimately resulting in the regulation of eIF4E-BP1, a key component of the protein translation machinery. A third Pi-stimulated and required cellular event is changes in energy metabolism including an increase in oxidative phosphorylation. Stimulation of these pathways have been identified in varying cell types in response to elevated extracellular Pi. Inhibitor studies suggest that the three pathways are required for different aspects of the Pi-induced alterations in cell functions related to altered gene expression, increased proliferation and metabolism, and angiogenesis.
