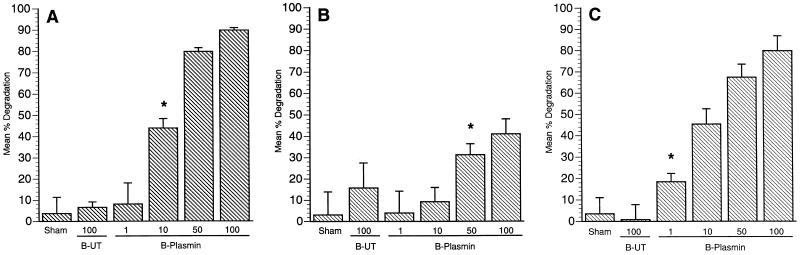
FIG. 2.
Degradation of soluble ECM components by graded concentrations of plasmin-coated B. burgdorferi. The substrates tested were fibronectin (A), laminin (B), and vitronectin (C). Spirochetes were incubated in HBSS with no additions (B-UT) and with addition of PLG and uPA together to form spirochete surface-associated plasmin (B-Plasmin). A sham preparation to control for free plasmin carryover in the latter group consisted of PLG and uPA in HBSS but no B. burgdorferi. ELISA plate wells (six replicates) coated with substrate were incubated for 6 h with a range of plasmin-coated B. burgdorferi concentrations (106, 10 × 106, 50 × 106, and 100 × 106 per well) as well as 100 × 106 untreated spirochetes. Undegraded substrate was detected, and percent degradation (a reduction in absorbance value was interpreted as substrate degradation) was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Bars represent mean substrate degradation relative to the positive control (0% degradation) ± the standard deviation of six replicate wells for each experimental group. ∗, statistically significant (P < 0.0001) compared to ELISA positive control. The experiment was performed twice with similar results.