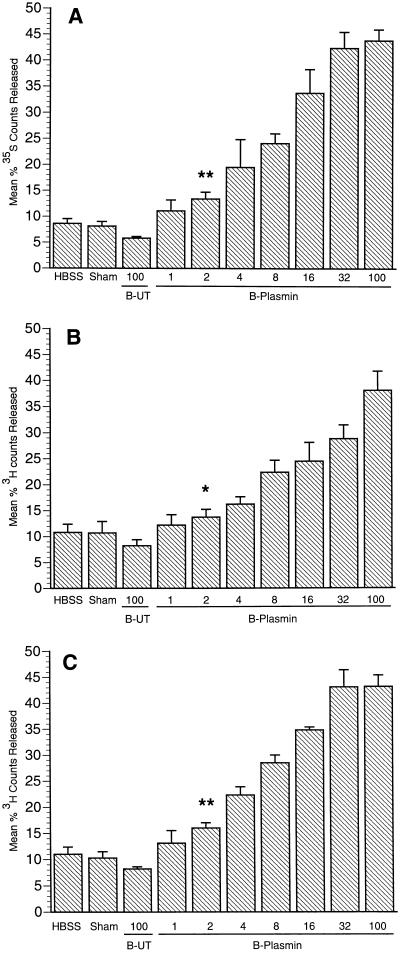
FIG. 4.
Degradation of radiolabeled, insoluble R22 ECM by graded concentrations of plasmin-coated B. burgdorferi. ECM components were labeled preferentially with [35S]methionine-cysteine (noncollagenous protein) (A), [3H]fucose (glycoprotein) (B), and [3H]proline (collagen) (C). Spirochetes were incubated in HBSS with no additions (B-UT) and with addition of PLG and uPA together in HBSS to form spirochete surface-associated plasmin (B-Plasmin). A sham preparation intended to control for free plasmin carryover in the latter group consisted of PLG and uPA in HBSS but no B. burgdorferi. Tissue culture plate wells containing labeled ECM were incubated for 6 h with a range of plasmin-coated B. burgdorferi concentrations (106, 2 × 106, 4 × 106, 8 × 106, 16 × 106, 32 × 106, and 100 × 106 per well) as well as 100 × 106 untreated spirochetes. Released (supernatant), and unreleased (2 N NaOH digest of undegraded ECM) radioactivity was counted for each well. Percent release of the total radioactive counts present in each well was calculated as described in Materials and Methods. Bars represent mean percent radioactivity release ± standard deviation of five replicate wells per experimental group. ∗, statistically significant (P < 0.05) compared to HBSS control; ∗∗, statistically significant (P < 0.001) compared to HBSS control. The experiment was performed twice with similar results.