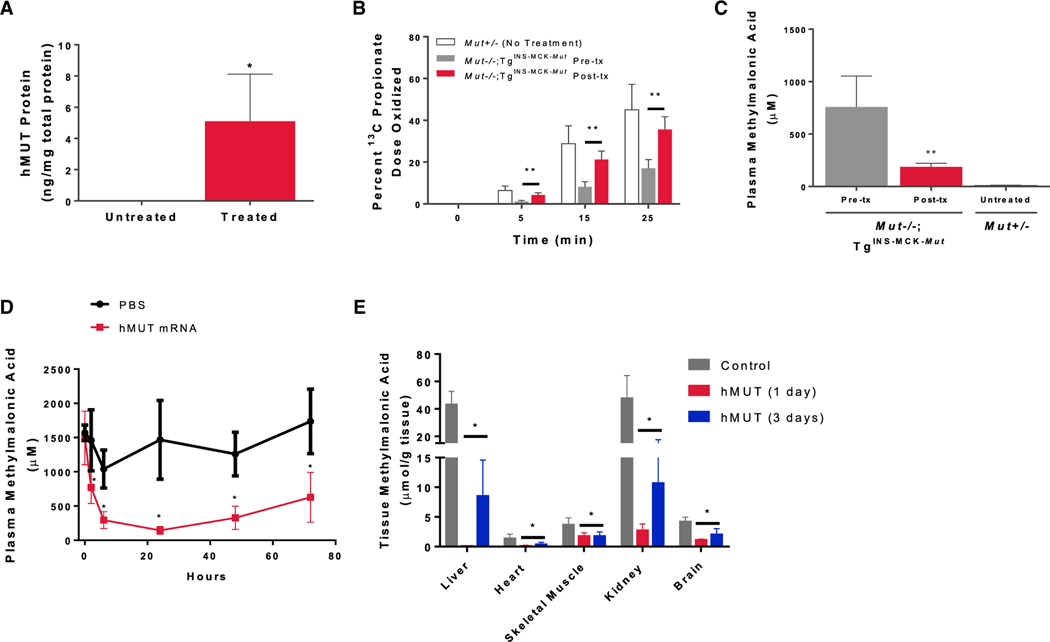
Figure 4. Single i.v. Dose of hMUT mRNA Increased Hepatic MUT Expression, Enhanced Propionate Oxidation, and Lowered Plasma and Tissue Methylmalonic Acid in Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut Mice.
Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut mice (n = 4) were administered a single i.v. dose (0.5 mg/kg) of hMUT mRNA encapsulated in LNP and sacrificed 3 days later.
(A) Hepatic MUT expression in Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut mice was quantified using LC-MS/MS.
(B) Propionate oxidation in Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut mice before and 3 days after hMUT mRNA treatment. The percentage of the administered 1-13C-propionate dose that was oxidized was determined by measuring 13C enrichment in expired CO2 at multiple time points.
(C) Plasma methylmalonic acid concentrations in Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut mice 3 days after hMUT mRNA treatment analyzed by LC-MS/MS.
(D) Plasma methylmalonic acid concentrations 1 day before, and 2, 6, 24, 48, and 72 hr after a single i.v. injection of hMUT mRNA (0.5 mg/kg) or PBS control in Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut mice (n = 4–8/group).
(E) Tissue methylmalonic concentrations in liver, heart, skeletal muscle (SM), kidney, and brain in PBS-injected control and hMUT mRNA (0.5 mg/kg)-treated Mut−/−;TgINS-MCK-Mut mice (n = 4–8/group). hMUT mRNA-treated mice were sacrificed at 1 day or 3 days after a single i.v. injection.
Data shown as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01. p values obtained from paired t tests to compare post-treatment versus pre-treatment values.