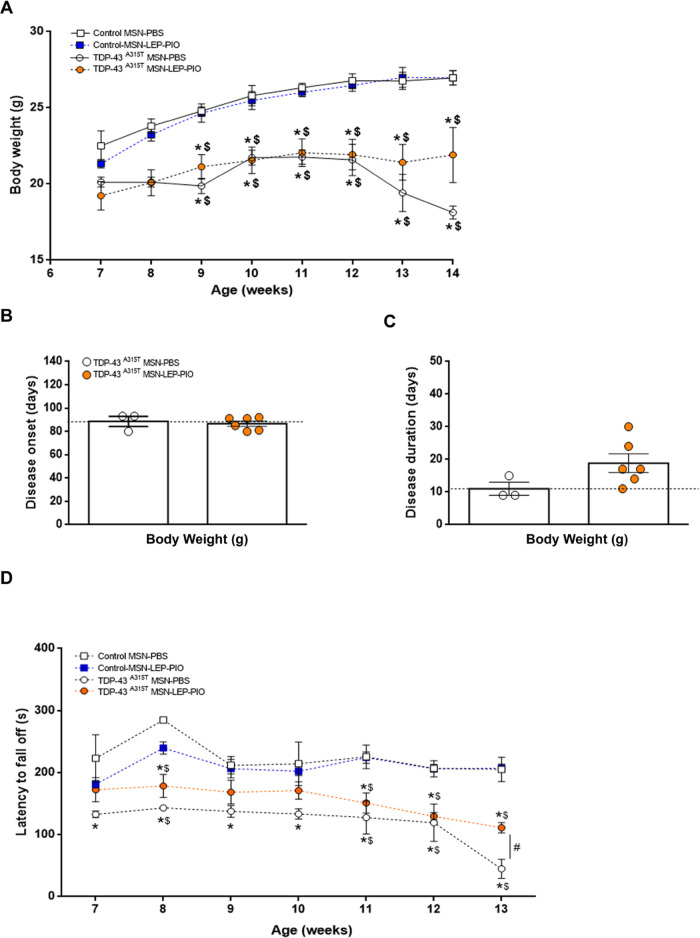
Figure 10.
MSN-LEP-PIO treatment beginning at the asymptomatic state of disease significantly enhances motor performance in TDP-43A315T mice. (A) Time monitoring of body weight was carried out in WT controls and TDP-43A315T mice IP treated with MSN-LEP-PIO or PBS. Starting weight in week 7. No significant differences were observed between MSN-LEP-PIO- or PBS-treated TDP-43A315T mice. (B) Average disease onset and disease duration (C) was determined in WT controls and TDP-43A315T mice IP treated with MSN-LEP-PIO or PBS using body weight as a physiological parameter. The average disease duration of the animal was calculated as the time between the onset of the disease (defined as the last day of individual peak body weight before a gradual loss occurs) and the day of death. Comparatively, the disease duration was higher in TDP-43A315T mice in response to MSN-LEP-PIO treatment. (D) Behavioral assessment of the motor function was performed in WT controls and TDP-43A315T mice IP treated with MSN-LEP-PIO or PBS over time. Significant differences between MSN-LEP-PIO- and PBS-treated mice were seen. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM. A comparison between groups was performed by two-way ANOVA, where *p < 0.05 vs PBS-treated WT control mice; $p < 0.05 vs MSN-LEP-PIO-treated WT control mice; and #p < 0.05 vs MSN-LEP-PIO-treated TDP-43A315T mice. Corresponding graphs as per (A), i.e., control–PBS (n = 3, white square and solid line), control–MSN-LEP-PIO (n = 3, blue square and dashed line), TDP-43A315T–PBS (n = 3, white circles and solid line), and TDP-43A315T–MSN-LEP-PIO (n = 6, orange circles and dashed line).