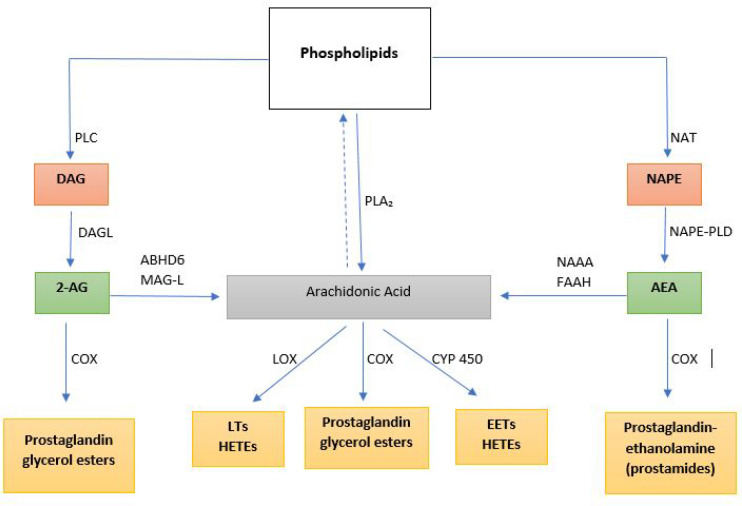
Figure 1.
Endocannabinoid anandamide (AEA) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) are formed from arachidonic acid-containing phospholipids. AEA is formed from a two-step catalysis of phospholipids to form N-arachidonoylphosphatidylethanolamine (NAPE). NAPE is cleaved by phospholipase D (PLD) to form AEA. AEA is metabolized by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and by N-acylethanolamine-hydrolyzing acid amidase (NAAA) to form arachidonic acid or by COX to form prostaglandin ethanolamide (prostamides). 2-AG is synthesized from diacylglycerol (formed from phosphoinositides by the action of phospholipase C) by the action of diacylglycerol lipase (DAGL). 2-AG is metabolized either via COX to form prostaglandin glycerol esters or by both monoacylglycerol lipase (MAG-L) and α,β-hydrolase domain-containing 6 (ABHD6) to form arachidonic acid. Additionally, arachidonic acid can be synthesized directly from phospholipids by phospholipase A2 (PLA2) which is further metabolized by lipoxygenase (LOX) to produce leukotrienes (LTs), cyclooxygenase (COX) to form prostaglandin glycerol esters, and cytochrome P450 (CYP) enzymes to form eicosanoids. EETs: epoxyeicosatrienoic acids; HETEs: hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids.