FIGURE 1.
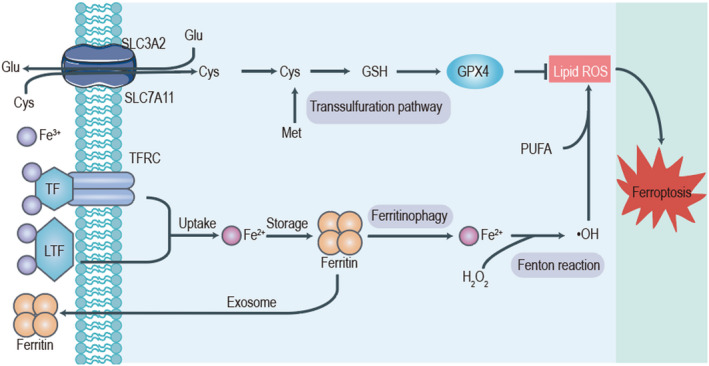
Mechanism of ferroptosis. The mechanism of ferroptosis involves two core parts: one is the xc‐GSH‐GPX4 system; the other is iron metabolism. System Xc‐ is composed of SLC7A11 and SLC3A2; it is responsible for transporting extracellular cystine into the cell and transporting intracellular glutamate out of the cell. Cystine is subsequently involved in the synthesis of GSH, an important antioxidant substance in cells that can inhibit ferroptosis. In addition, transferrin (TF) and lactotransferrin (LTF) import iron into cells. Excessive free Fe2+ induces the production of lipid reactive oxygen species (ROS) through the Fenton reaction and ultimately promotes the occurrence of ferroptosis in the cell.
