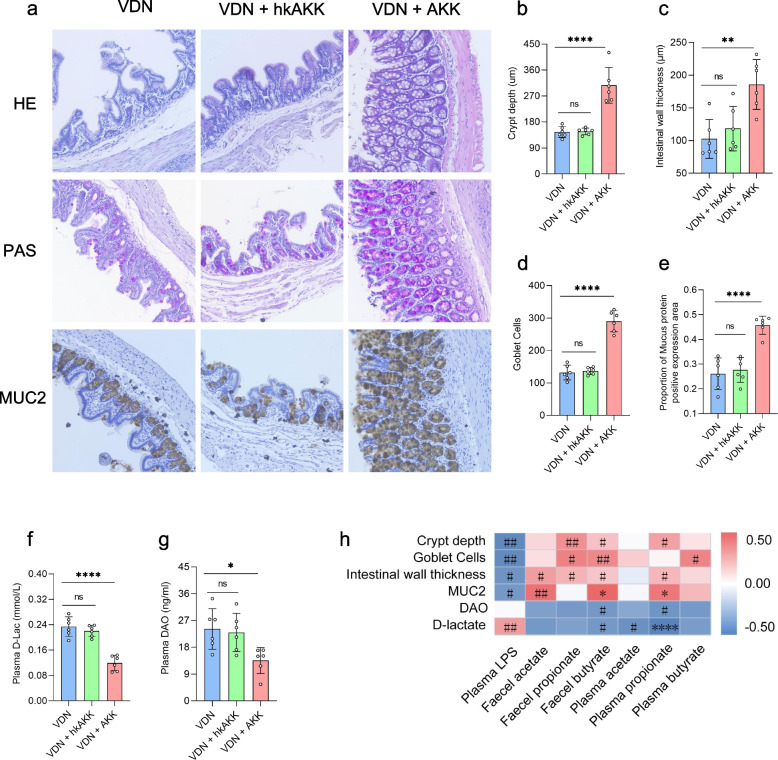
Fig. 10.
Alleviation of intestinal mucosal barrier impairment in VDN-treated rats by Akkermansia. Typical haematoxylin-eosin (HE) staining, periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining and MUC2 immunohistochemical staining for intestinal tissues (original magnification ×200). b–e Parameters of crypt depth, intestinal wall thickness, goblet cell count and MUC2 expression levels, respectively. f, g Plasma D-lactate and diamine oxidase contents, respectively. h Spearman’s correlation analysis of the relationship of SCFAs and LPS with intestinal barrier-related parameters (e.g. crypt depth, intestinal wall thickness, MUC2 level and goblet cell count). Red and blue denote positive and negative correlations, respectively. Data are presented as the mean±standard deviation (SD). Statistical significance was determined using one-way ANOVA (Tukey post hoc test). NS for P > 0.05, #P < 0.25, ##P < 0.1, *P< 0.05, **P< 0.01, ***P< 0.001, ****P< 0.0001