FIGURE 7.
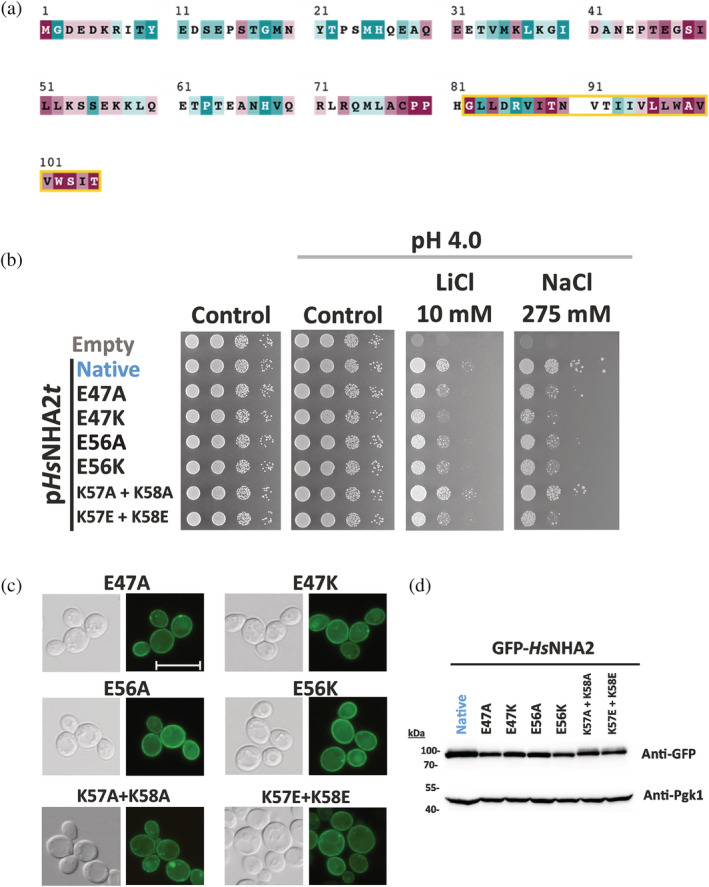
Charged residues in HsNHA2 hydrophilic N‐terminus are important for transport activity. (a) Evolutionary conservation analysis of HsNHA2 N‐terminus. HsNHA2 N‐terminal residues 1‐to‐105 colored based on ConSurf server evolutionary conservation scale, with cyan to maroon representing variable to conserved amino acids, respectively. The position of the unique N‐terminal TMS is highlighted with a yellow box. The conservation analysis was conducted using HsNHA2 N‐terminal amino acids. A total of 99 unique sequences were collected by HMMER from the UniRef90 database with sequence identity ranging from 35 to 95% and an E‐value of at least 0.00001. (b) Salt tolerance of S. cerevisiae BW31 cells containing empty vector or expressing native HsNHA2 or one of six HsNHA2 mutated versions E47A, E47K, E56A, E56K, K57A + K58A, or K57E + K58E from pHsNHA2t. Cells were grown on YNB‐Pro or non‐buffered YNB‐Pro plates with the pH adjusted to 4.0 and supplemented with LiCl or NaCl as indicated. Plates were incubated at 30°C for 2 (controls) or 5 days (salts). Localization (c) and immunodetection (d) of N‐terminal GFP‐tagged HsNHA2 mutated versions as in (b). BW31 cells expressing variants of GFP‐HsNHA2 from the pGFP‐HsNHA2t were grown in YNB‐Pro (4% glucose) to the exponential phase and observed under a fluorescence microscope (c, right). A Nomarski prism was used for whole‐cell imaging (c, left). The scale bar corresponds to 10 μm. In (d), protein extracts from the same cells as in (c) were prepared as described in Section 5, subjected to SDS‐PAGE (10% gel) and transferred to a nitrocellulose membrane. GFP‐HsNHA2 variants were detected with an anti‐GFP antibody. The membrane was reprobed and incubated with an anti‐Pgk1 antibody to verify the amount of loaded proteins
