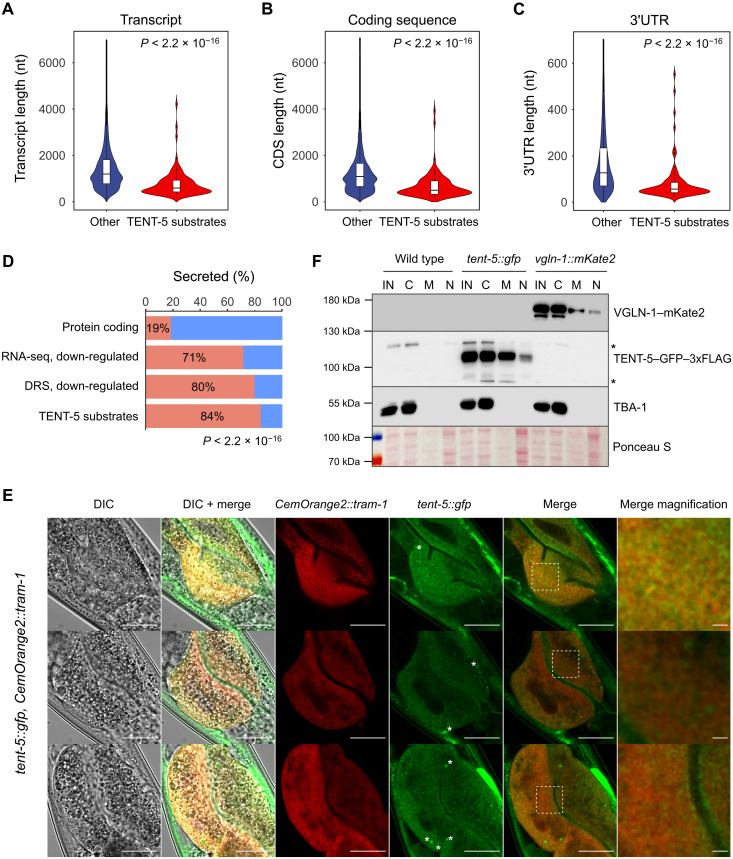
Fig. 6. TENT-5 regulates mRNAs that encode secreted proteins.
Violin plots showing length distribution of transcripts (A), coding sequence (B), and 3′UTRs (C) of TENT-5 substrates (n = 96) compared to other transcripts identified by DRS (n = 16,568) (P value, Wilcoxon test). (D) Fractions of genes that encode secreted proteins (red) as defined in (60) across indicated datasets: expressed protein-coding genes (WS270; RNA-seq, base mean > 0), RNA-seq and DRS tent-5(tm3504) down-regulated genes [FDR < 0.05, log2FC < −log2(1.5)], and TENT-5 substrates. P value for enrichment of genes encoding secreted proteins in each group versus whole genome is <2.2 × 10−16 (Fisher’s exact test). (E) Representative fluorescence and DIC microscopy images of distal parts of the adult worms’ intestines, which coexpress TENT-5-GFP and ER marker protein CemOrange2–TRAM-1. Both tagged proteins partially colocalize at the ER (Pearson correlation coefficient: 0.4 ± 0.11 SD, 18 worms). Analysis was restricted to cells expressing CemOrange2–TRAM-1, and the strongest unspecific signal from the green channel (examples are marked with asterisks) was excluded from the analysis. White dashed squares in the merge picture indicate the region magnified on the right. Scale bars, 20 μm (all pictures) and 2 μm (magnification). (F) TENT5C is present in the ER fraction. Subcellular fractionation of proteins isolated from wild-type, tent-5::gfp::3xflag, and vgln-1::mKate2:::3xmyc strains followed by Western blot. Anti-tubulin (TBA-1) and anti–red fluorescent protein (VGLN-1–mKate2) antibodies and Ponceau S staining were used as fractionation controls. IN, input; fractions: C, cytoplasmic; M, membrane; N, nuclear. Asterisks indicate nonspecific bands.