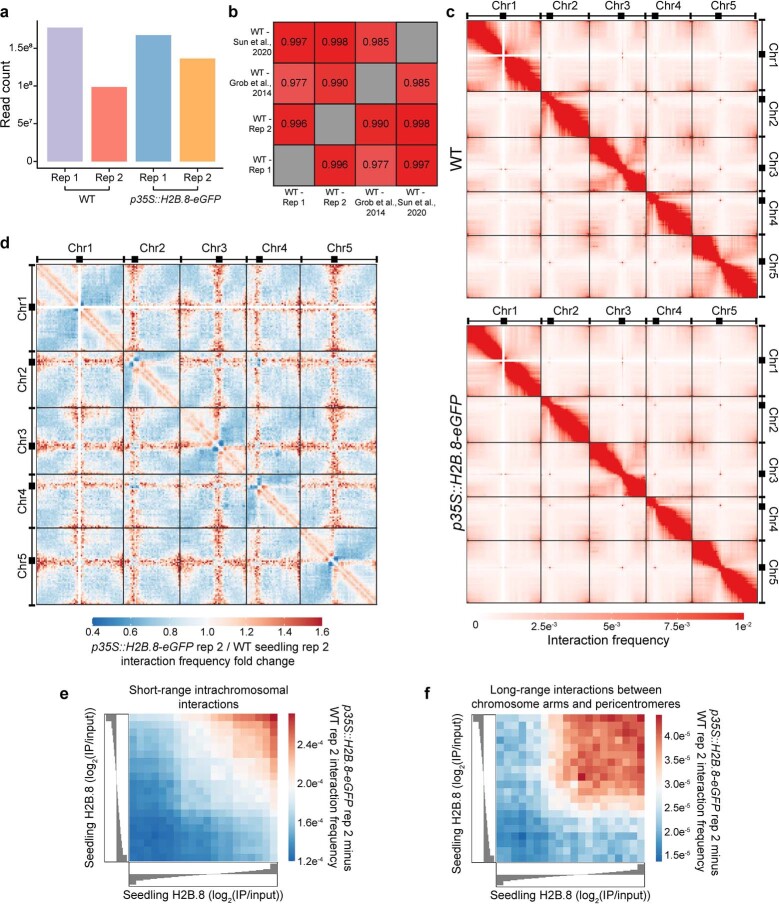
Extended Data Fig. 7. H2B.8 affects intra- and inter-chromosomal interactions.
a, Sequencing read counts of wild-type (WT) and p35S::H2B.8-eGFP seedling Hi-C libraries. Rep, biological replicate. b, Correlations between the Hi-C data generated in this study and previously published36,37. R, Pearson’s correlation coefficient. c, Hi-C interaction frequency heatmaps at 500 kb resolution for WT (upper; merged replicates) and p35S::H2B.8-eGFP (lower; merged replicates) seedlings. d, Genome-wide interaction frequency fold change heatmap between WT (Rep 2) and p35S::H2B.8-eGFP (Rep 2) seedlings at 500 kb resolution, as shown in Fig. 6a for Rep 1. e, Short-range intrachromosomal interaction frequency difference between p35S::H2B.8-eGFP (Rep 2) and WT (Rep 2) over quantiles of seedling H2B.8 enrichment (log2(IP/input)), as shown in Fig. 6b for Rep 1. Spearman’s ρ = 0.930. f, Long-range interaction frequency difference between p35S::H2B.8-eGFP (Rep 2) and WT (Rep 2) between chromosome arms and pericentromeric regions over quantiles of seedling H2B.8 enrichment (log2(IP/input)), as shown in Fig. 6c for Rep 1. Spearman’s ρ = 0.870.