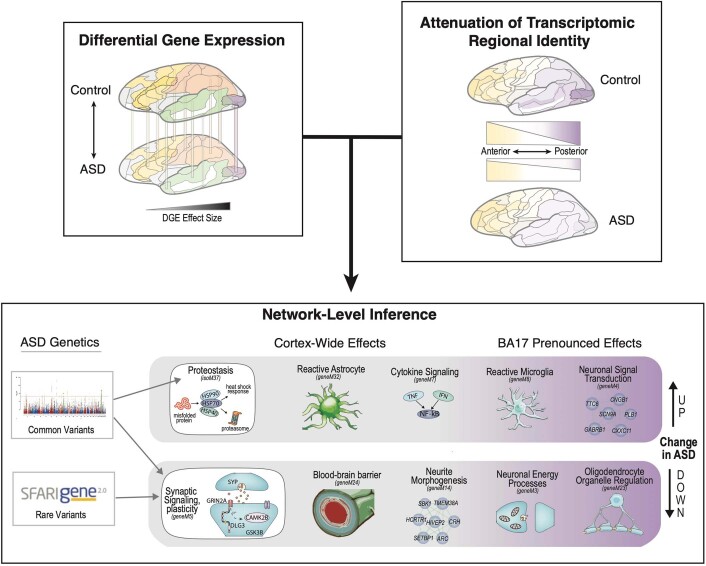
Extended Data Fig. 10. Results Summary.
Overview of results from this pan-cortical characterization of the ASD transcriptome. Top left, differential gene expression signatures in ASD, while observed cortex-wide, show greatest effect size changes in posterior regions, especially BA17. Top right, a widespread posterior-predominant attenuation in transcriptomic regional identity is observed in ASD. Bottom, co-expression networks provide an organizing framework for interpretation of cortex-wide and regionally variable effects. A cortex-wide, upregulated co-expression module (isoM37) comprised of genes involved in proteostasis is enriched for common ASD-associated genetic variation. A cortex-wide, downregulated module characterized by genes involved in synaptic signaling and plasticity showed enrichment for common and rare genetic risk variants. Other modules exhibiting cortex-wide or regionally pronounced differential expression patterns in ASD are highlighted.