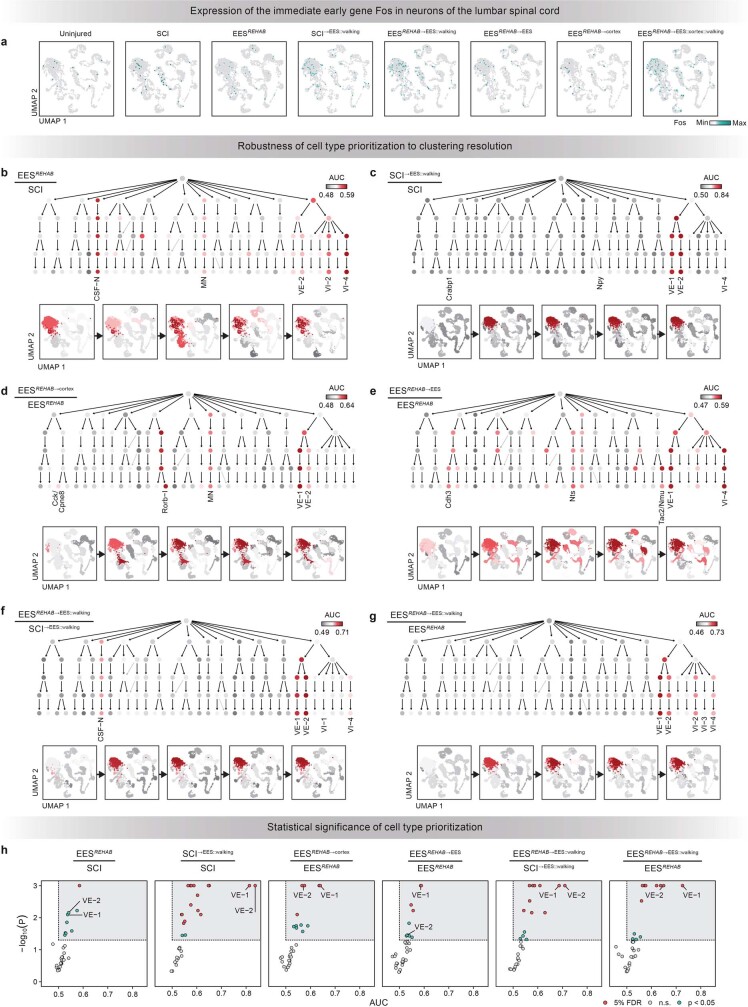
Extended Data Fig. 8. Cell type prioritization to identify recovery-organizing neurons.
a, Expression of the immediate early gene cFos in neuronal nuclei from each of eight experimental conditions. b–g, Robustness of cell type prioritizations across six comparisons capturing the key therapeutic features of EESREHAB. Top, cell type prioritizations are shown within a clustering tree of spinal cord neurons declined in five different clustering resolutions, demonstrating the robustness of these prioritizations to the resolution at which transcriptionally defined neuronal subpopulations are defined. The five cell types with the highest AUCs in each comparison are annotated. Bottom, cell type prioritizations over increasingly granular clustering resolutions are visualized on a progression of UMAPs, with neuronal subpopulations colored by the strength of the perturbation response, as inferred by Augur. h, Volcano plots showing the strength of the perturbation response (x-axis) and its statistical significance (permutation test, y-axis) for six direct comparisons between two experimental conditions each capturing the key therapeutic features of EESREHAB.