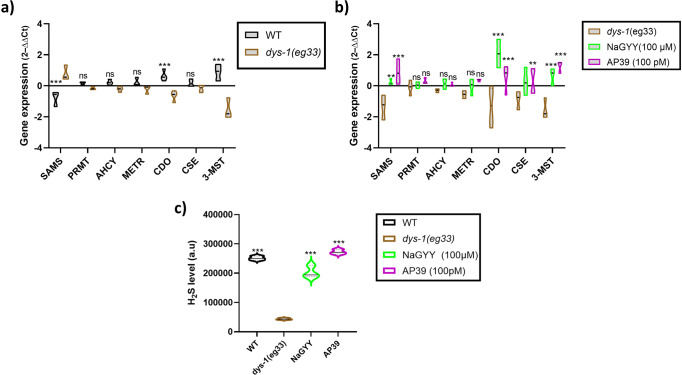
Fig. 1. DMD animals have alterations in sulfur metabolism and reduced H2S levels.
a Relative quantification mRNA levels of enzymes associated with sulfur metabolism in wt and dys-1(eg33) animals. An increase can be seen in SAMS (s-adenosylmethionine synthetase), CDO (cysteine dioxygenase) and 3-MST (3-mercaptopyruavate transferase) in dys-1(eg33) animals. b Increased expression can be seen in SAMS, CDO, CSE (cystathionine-γ-lyase) and 3-MST with NaGYY and AP39 treatment. There were no differences in PRMT (methyl transferase), AHCY (s-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase) or METR (methionine synthase). Data are mean ± SD from three biological repeats using 150–200 animals. Results were analysed with a two-way ANOVA. All significance points are compared to dys-1(eg33). ***P < 0.0001, **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05, ns P > 0.05. c Fluorescence intensity of the AzMC signal, normalised to protein content. There is a decline in global H2S levels in the dys-1(eg33) animals compared to wt, which is increased by NaGYY and AP39 treatment. Data for each treatment are from 270 animals across three biological repeats. Results were analysed with a one-way ANOVA. All significance points are compared to dys-1(eg33). ***P < 0.0001.