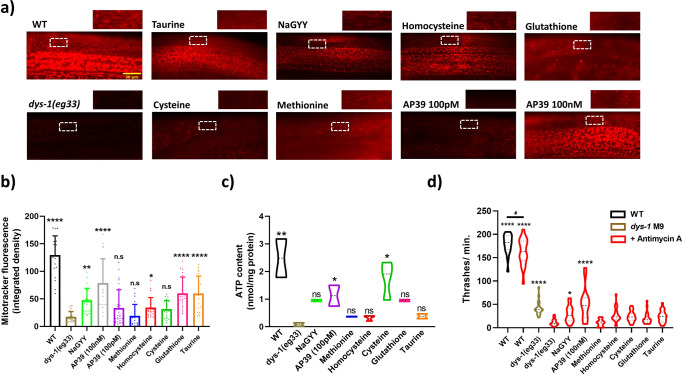
Fig. 5. H2S compounds show greater mitochondrial function improvements to SAA in dys-1(eg33) mutants.
a Representative images of mitotracker fluorescence uptake. Cut away images are of mitochondria within body-wall muscle to highlight fluorescence signals. Scale bar: 30 µm. b Quantification of Mitotracker fluorescence. Untreated dys-1(eg33) animals exhibit significant declines in mitochondrial membrane potential to wt. Treatment with 100 μM NaGYY and 100 nM (but not 100 pM) AP39 were able to significantly improve membrane potential. In addition, L-taurine, L-homocysteine and L-glutathione (but not L-cysteine and L-methionine) were able to significantly augment mitochondrial membrane integrity in dys-1(eg33) mutants. Data are mean + SD of two biological repeats, with 50–60 animals per condition. Asterisks denote significance to untreated dys-1(eg33) animals (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ****P < 0.0001). c There is a decline in ATP content in dys-1(eg33) animals. Treatment with AP39 (100 pM) and L-cysteine significantly increased ATP content. The other SAA trialled did not induce a significant improvement in ATP content. Data for each treatment are from 270 animals across three biological repeats. **P < 0.01, *P < 0.05. d Complex III inhibition induces significant movement decline in dys-1(eg33) that is restored with AP39 (100 nM) and NaGYY administration, but not SAA. Data are obtained from two biological repeats with 30–40 animals per condition. Asterisks denote significance to dys-1(eg33) + Antimycin A exposure (*P < 0.05, ****P < 0.0001). ‘#’ denote significance between wt treatments (#P < 0.05).