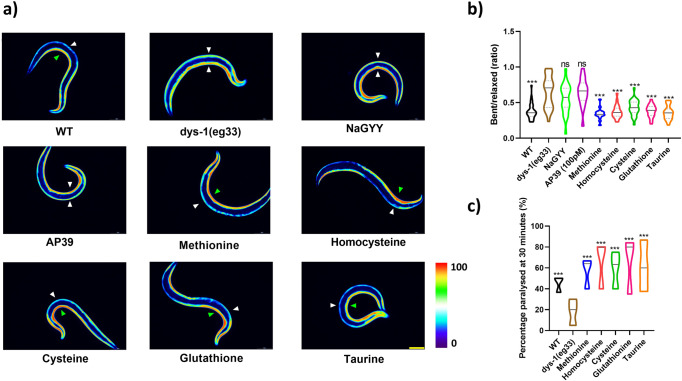
Fig. 7. Calcium mishandling is improved in the dys-1(eg33) animals treated with SAA.
a Representative images of calcium report strain in HBR4 (wt), HBR4xBZ33 (dys-1(eg33)) and HBR4xBZ33 treated with H2S and SAA: L-methionine (10 mM), L-homocysteine (10 µM), L-cysteine (10 µM), L-glutathione (100 µM) and L-taurine (10 µM). In wt animals, high levels of calcium can be detected on the contracted side (green arrow) of the body-wall muscles with no calcium being detected on the relaxed side (white arrow). In dys-1(eg33) animals, high levels of calcium can be detected on both the relaxed and contracted sides. Treatment with SAA restored calcium handling to that which represented wt. b Quantification of the relative ratio of calcium intensity for bent (contracted) side vs relaxed side. The ratio is higher than wt in dys-1(eg33) and is restored by treatment with SAA. Both NaGYY and AP39 were unable to confer significant improvements in calcium handling. Data are from 20 animals across two biological repeats. Scale bar: 30 µm. c dys-1(eg33) animals are resistant to levamisole after 30 min of exposure compared to wt. This is improved by all SAA. Data are from 30 animals across three independent biological repeats. Results were analysed with a two-way ANOVA. All significance points were compared to dys-1(eg33). ***P < 0.0001, ns P > 0.05.